Original Studies
AIM: To assess the prevalence of chronic kidney disease (CKD), clinical and demographic characteristics and therapy profile in patients with type 2 diabetes admitted to multidisciplinary hospitals. CREDO (Cardio-REnal Diabetic cOmplications) trial was initiated for this purpose.
MATERIALS AND METHODS: in a prospective observational multicenter study for the period from August 2022 to April 2023, data from 445 patients with type 2 diabetes hospitalized in multidisciplinary hospitals of the Moscow Department of Health were analyzed. The data was collected on a single visit. The design of the study did not involve any interventions in routine clinical practice, including the choice of a diagnostic or treatment method.
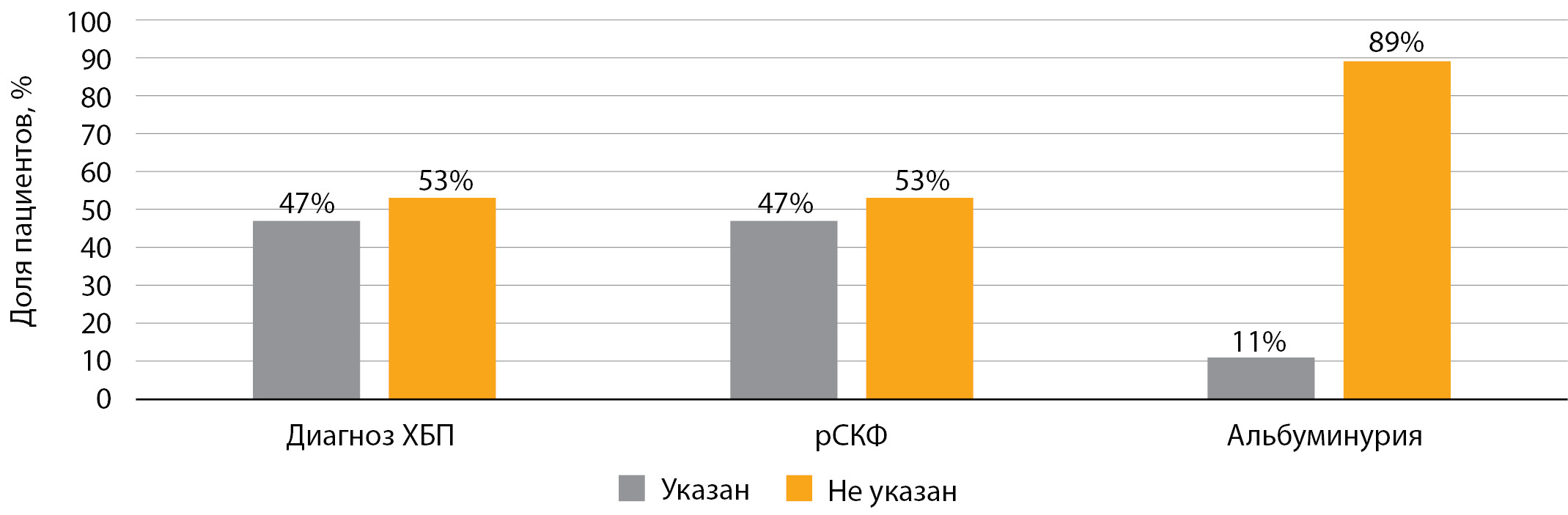
RESULTS. The study included 445 patients with the main inclusion criteria — type 2 diabetes, age over 50 years, duration of diabetes more than 3 years. The prevalence of CKD was 90%, while in 43% the diagnosis of CKD was confirmed, in 43% it was detected for the first time, and in 7% the disease progressed. Patients with stage C2 and C3 (a and b), as well as with levels of A1 and A2 albuminuria, were most often identified. The percentage of patients in whom the albuminuria was not performed remained high — 46.2%. The highest incidence of CKD was observed in patients with inadequate glycemic control, having an HbA1c level of ≥9%. In the group with newly diagnosed CKD, sodium-glucose co-transporter-2 inhibitor (iSGLT-2) was received by 31.1% of patients, glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RA) — 7.9% of patients. In the group with confirmed CKD — 30.7% and 9.4%, respectively.
CONCLUSION: it has been shown that patients over the age of 50 with type 2 diabetes with a disease duration of more than 3 years are at a high risk of developing CKD — 90%. The results obtained convincingly confirm the possibility of detecting CKD and initiating nephroprotective therapy at the hospital stage.
BACKGROUND: Increased glucose variability is recognized as a risk factor for vascular diabetic complications. It is assumed that deteriorating effect of GV on blood vessels can be realized through the activation of inflammatory signaling pathways.
AIM: to determine associations of low-grade inflammation markers and serum cytokines with time in ranges and GV parameters derived from continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) in patients with type 1 diabetes (T1D).
MATERIALS AND METHODS: In 470 adult patients with T1D, high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hsCRP) and fibrinogen was measured, neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) and the Systemic Immune-inflammation Index (SII) were calculated. In a sample of 130 patients and 20 healthy individuals (control), serum concentrations of interleukins (IL-1β, IL-4, IL-6, sIL-6Rα, IL-19, IL-20, IL-22, IL-26, IL-27, IL-28A, IL-29, IL-32, IL-34, IL-35) were assessed by multiplex analysis. Time in the ranges and GV parameters: Coefficient of Variability (CV), Mean Amplitude of Glycemic Excursions (MAGE), and Mean Absolute Glucose rate of changes (MAG) were derived from CGM data.
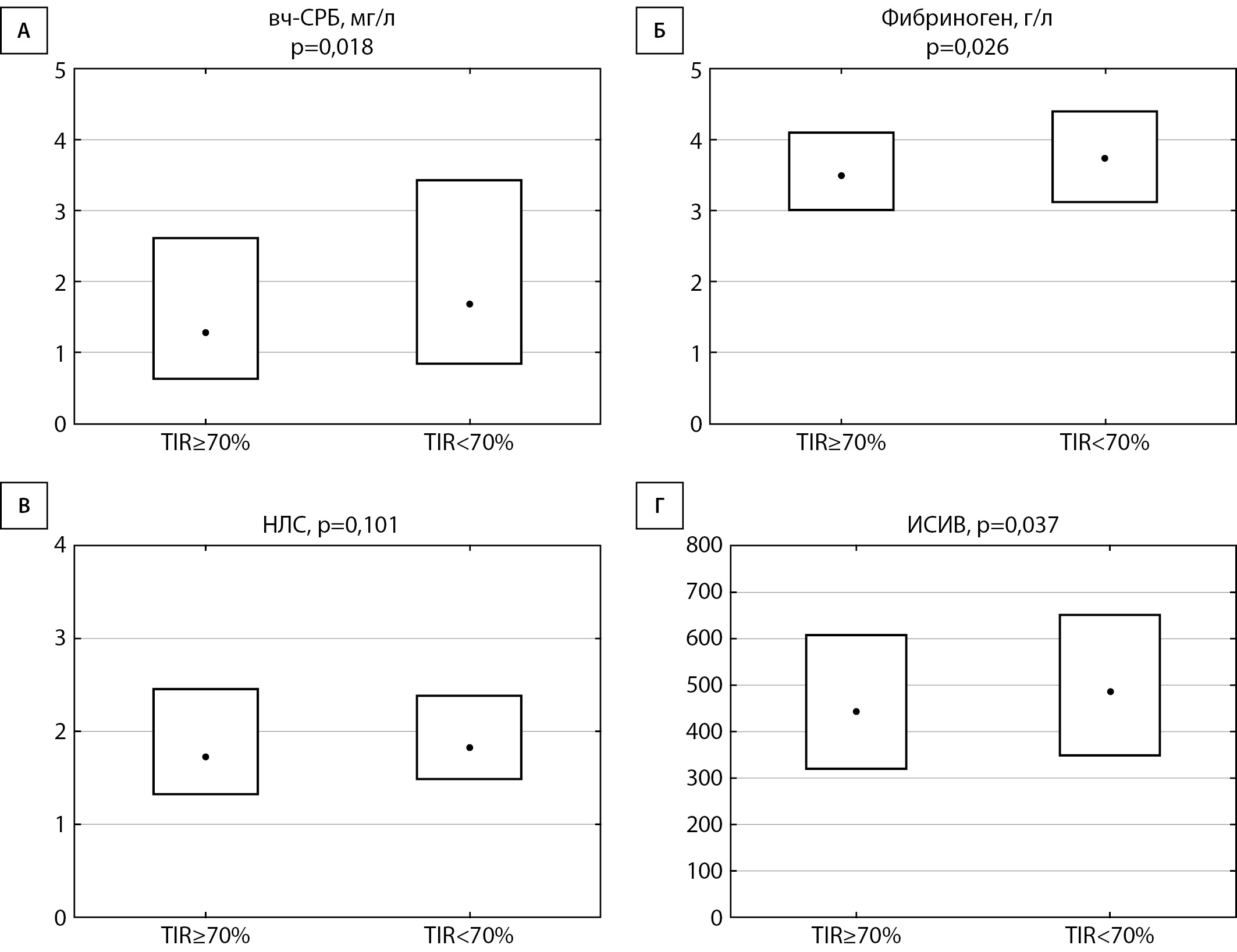
RESULTS: Patients with Time In Range (TIR) <70% had higher concentrations of hs-CRP and fibrinogen, higher SII values, and demonstrated a trend toward higher TIR compared with those with TIR ≥70% (p=0.018, p=0.026, p=0.037, p=0.101, respectively). Patients with T1D, when compared to control, demonstrated increased concentrations of IL-1β (p<0.0001), IL-6 (p<0.0001), decreased levels of IL-4 (p=0.002), and a tendency to decrease IL-22 and IL-29 (p=0.1). Patients with TIR>70% had higher levels of IL-4 (p=0.02) as well as lower concentrations of IL-1β (p=0.0003) and IL-6 (p=0.007) than patients with TIR≤70%. In a multivariate stepwise regression analysis including clinical data and CGM parameters as independent variables, body mass index was positive predictor of hsCRP and fibrinogen levels, TIR was negatively associated with IL-20 and IL-34, time above range was associated positively with IL-1β, MAGE showed positive association with SII, IL-26 and IL28A, while MAG was positively associated with IL-29.
CONCLUSION: T1D patients with non-target TIR (<70%) have higher levels of low-intensity inflammatory markers and serum pro-inflammatory cytokines than patients with TIR>70%. Both hyperglycemia and increased GV are associated with intensity of low-grade inflammation in T1D.
BACKGROUND: Previous studies have shown that, the triglyceride glucose index (TyG index) is related with the development of cardiovascular disease.
AIM: Our novel study aimed to determine whether the TyG index measured at the time of diagnosis conducted on newly diagnosed type 2 diabetic individuals and the relationship between TyG index and carotid intima media thickness, as well as both myocardial functions and epicardial adipose tissue was investigated.
MATERIALS AND METHODS: The study included 105 individuals (58 F, 47 M; mean age 50.4±9.8 years) newly diagnosed with T2DM and 51 healthy subjects (30 females, 21 males, mean age 49.8±8.9 years) without any chronic disease as the control group. In addition to laboratory parameters, transthoracic echocardiography carotid intima-media thickness with linear vascular probe were examined in all individuals.
RESULTS: TyG index was significantly higher in newly diagnosed type 2 diabetic individuals compared to the controls. There was a positive correlation between the TyG index and carotid intima-media thickness, epicardial fat thickness, HbA1c, Homa-IR, body surface area, waist circumference, hip circumference, body mass index and CRP. When diastolic functions were considered, there was a negative correlation with E/A and a positive correlation with E/e’ septal. TyG index was also negatively correlated with EF. Regression analysis revealed that age and TyG index were associated with an increase in carotid IMT thickness.
CONCLUSION: TyG index measured at the time of diagnosis in newly diagnosed type 2 diabetic patients is also associated with subclinical atherosclerosis, deterioration in left ventricular systolic and diastolic functions.
BACKGROUND: The results of surgical treatment of rectal fistulas (RF) directly depend on the accuracy of their diagnosis and the detection of a concomitant disease, such as diabetes mellitus (DM). To improve the results of surgical treatment, it is necessary to take into account the mutual influence of RF and DM, which can aggravate each other’s course.
AIM: The study of the features of the course of RF against the background of DM and the assessment of their mutually aggravating influence.
MATERIALS AND METHODS: 120 patients with RF were studied, which were divided into two groups: the main group (MG) included 60 patients with DM, the control group (CG) also included 60 patients without DM.
RESULTS: In both groups, patients with transsphincteric RF dominated: 39 (65.0%) in the MG and 38 (63.3%) in the CG. Recurrent SPC prevailed in patients with DM (30.0% versus 15.0%), which indicates a more complex course of RF against the background of DM. It was found that in 17 (28.3%) patients, the stage of diabetes compensation after the formation of a fistula with a purulent cavity in the pararectal tissue passed into the stage of subcompensation and, due to an unstable decrease in blood sugar levels, it was necessary to replace tableted antidiabetic drugs with injectable insulin, which says about the deterioration of the course of diabetes against the background of chronic purulent inflammation in the pararectal tissue. The results of the study showed the presence of a direct correlation between the course of chronic paraproctitis and the stage of DM (r=0.50552, p<0.001), which indicates the presence of a mutual burden syndrome.
CONCLUSION: DM and chronic paraproctitis have a mutually aggravating effect on each other. Our results indicate the presence of a syndrome of mutual aggravation in patients with RF fistulas against the background of DM, which worsen the course of each other, which must be taken into account at the stages of diagnosis and preoperative preparation of patients to improve the immediate and long-term results of surgical treatment in this category of patients.
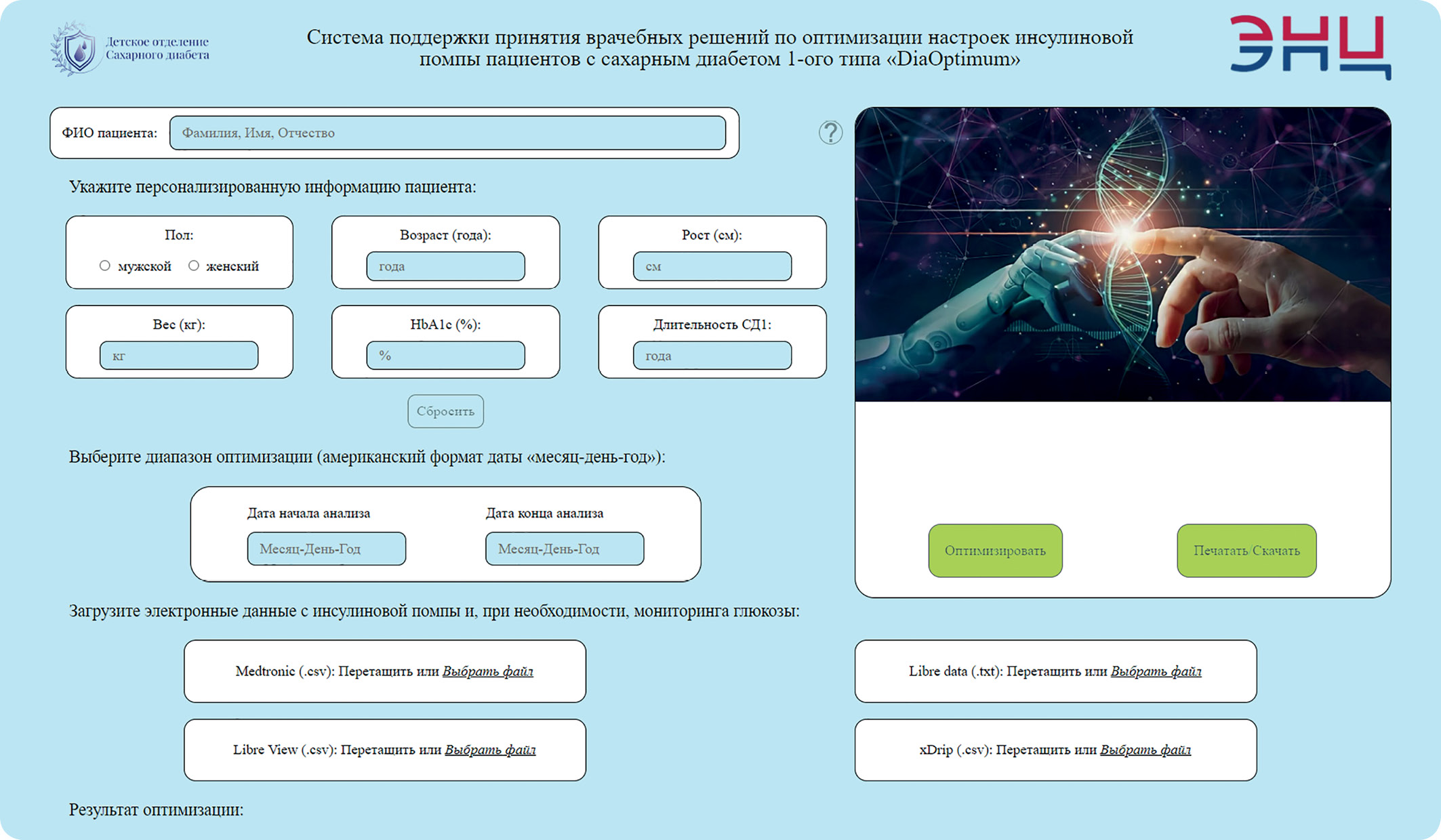
BACKGROUND: Widely available diabetes devices (continuous glucose monitoring, insulin pump etc.) generate large amount of data and development of an advanced clinical decision support system (CDSS), able to automatically evaluate and optimize insulin therapy, is relevant.
AIM: Development of a mathematical model and an CDSS based on it to optimize insulin therapy in children with type 1 diabetes (T1D) and assessment of the agreement between the recommendations of the CDSS and the physician on insulin pump (IP) parameters: basal profile (BP), carbohydrate ratio (CR), correction factor (СF).
MATERIALS AND METHODS: Data from 504 children with T1DM were analyzed over the period of 7875 days. The data included glucose, insulin, food, sex, age, height, weight, diabetes duration and HbA1c. We constructed recurrent neural network (RNN) to predict glucose concentration for 30-120 minutes, an algorithm for optimizing IP settings using prediction results. Next, a software product was developed — a CDSS. To assess the agreement of the recommendations of the CDSS and physicians, retrospective data from 40 remote telemedicine consultations of 40 patients with T1D (median age 11.6 years [7; 15]) were used and 960 points of possible adjustments were analyzed. Three degrees of agreement have been introduced: complete agreement, partial agreement, and complete disagreement. The magnitude of the adjustments was also analyzed.
RESULTS: The accuracy of glycemic predictions was better or comparable with other similar models. The assessment of agreement for BP, CR and CF, according to the Kappa index, showed slight and weak agreement. The frequency of complete agreement between recommendations for adjusting the ongoing IP therapy between the CDSS and physicians is 37.5–53.8%, and complete inconsistency is 4.5–17.4%. From a clinical point of view, consistency in the frequency of occurrence of the indicator is more important. There were no differences in median IP settings between the CDSS and physicians.
CONCLUSION: The CDSS has an acceptable accuracy of glycemic predictions. The CDSS and physicians provide comparable recommendations regarding CSII parameters.
BACKGROUND: Previously, we presented the process of developing a clinical decision support system (CDSS) for adjusting insulin pump (IP) settings in children with type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1D) and assessing the agreement of the recommendations it generates with the expert opinion. The CDSS demonstrated satisfactory forecasting of glucose profile and agreement rates between recommendations CDSS and experts.
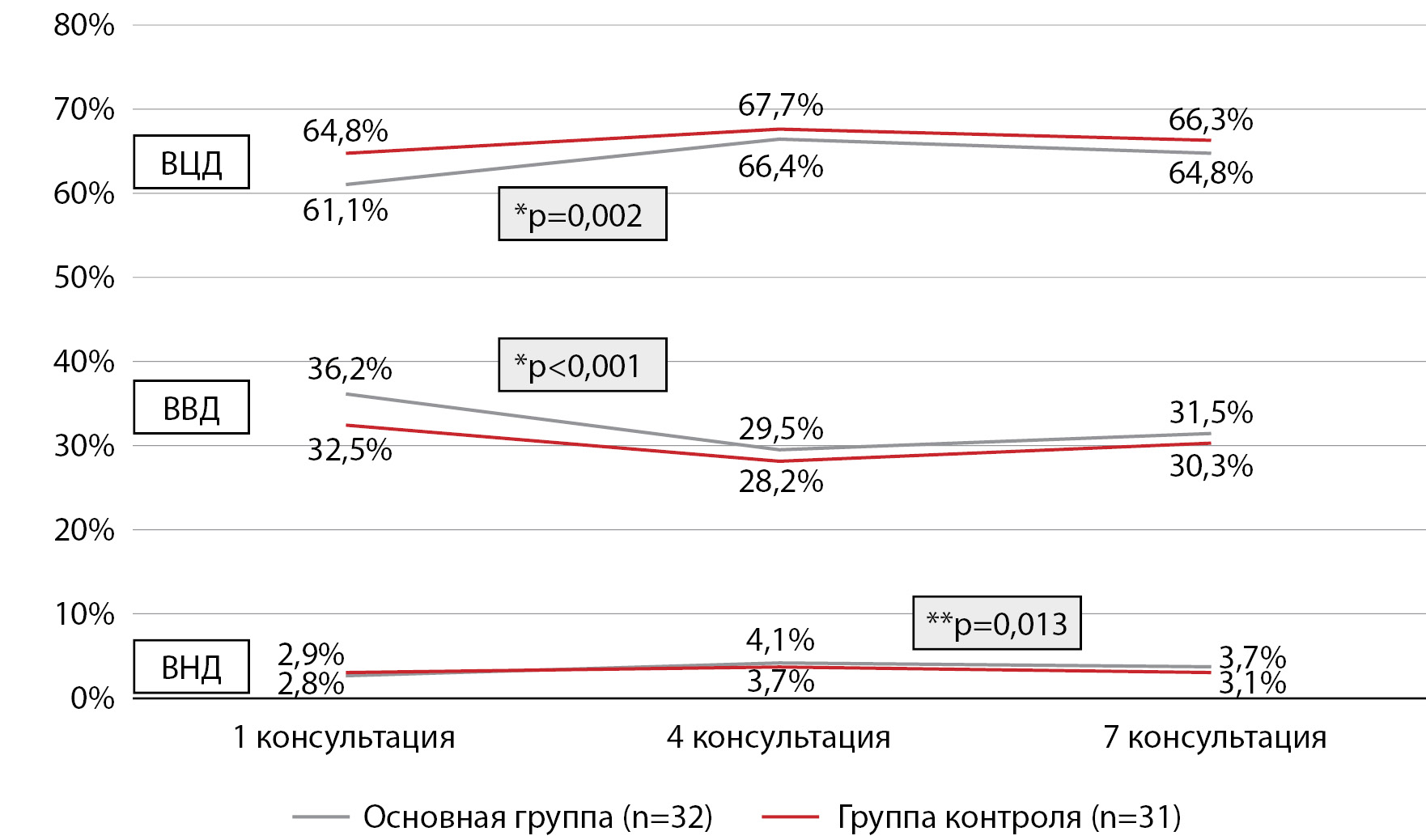
AIM: To evaluate the effectiveness and safety of using CDSS in children with T1D, testing the hypothesis of non-inferiority (with a limit of -5%) of relative increase of glucose time in range (TIR) over 6 months.
MATERIALS AND METHODS: The trial included 80 children with T1D, divided into two comparable groups of 40 children using the minimization method. Patients in the main group received recommendations for adjusting the IP settings from a physician who uses the CDSS; patients in the control group received recommendations from a physician (control group). Patients were observed for 6 months with remote consultations once a month (7 consultations in total) and monitoring of glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) at 1, 4 and 7 consultations. The primary outcome is the difference in group mean relative changes in TIR (%), secondary outcomes are TIR (%), HbA1c concentration.
RESULTS: The trial was completed by 63 patients 32 in the main group, 31 in the control group. The difference in the mean relative increase in TIR at the 7th consultation in the groups was 3.02%, one-sided 95% CI (-4.55%; inf ). Thus, the lower bound of this CI is greater than the noninferiority limit of -5%, and the noninferiority hypothesis can be accepted. There were no statistically significant differences between groups for all outcomes. The dynamics of the indicators were positive in the main group and had a statistical tendency towards positive changes in the control group.
CONCLUSION: The use of CDSS was no less effective in terms of the TIR than the management of the patient by a physician. The use of CDSS in clinical practice can help in regular and frequent monitoring of children with T1D, and standardize at a high level the approach to correction of IP parameters, supplemented with CGM.
OBJECTIVE: Clinical and economic evaluation of using the dapagliflozin in addition to standard therapy for patients with CHF (Chronic Heart Failure) and concomitant type 2 DM (Diabetes mellitus).
MATERIALS AND METHODS: All adult Russian patients with confirmed diagnosis of CVD and concomitant type 2 DM were considered as the target population. We evaluated the use of dapagliflozin in addition to standard therapy in comorbid patients with CHF and DM type 2 on the indicators of CC death, death from any cause of hospitalization due to CHF, emergency treatment due to CHF, as well as calculated the cost per life year saved and quality-adjusted life year (QALY) saved both when using standard therapy alone and in combination with dapagliflozin.
RESULTS: The use of dapagliflozin in addition to standard therapy for the treatment of comorbid patients with CHF and DM 2 per cohort of 1,000 people will prevent an additional 1,3 and 10 years:
- CHD-related hospitalizations: 40, 99, 195, respectively;
- Emergency admissions due to CVD: 15, 38, 73 respectively;
- CC deaths: 9, 19, 25 respectively;
- Deaths from any cause: 10, 21, 19
At the same time, the costs per one year of quality-adjusted life saved were 1,923,509 rubles during the first year, 1,102,680 rubles during the first 3 years, and 560,841 rubles for 10 years, which did not exceed the calculated value of the willingness-to-pay threshold — 3.14 million rubles, and allowed us to conclude that dapagliflozin is clinico-economically feasible in the studied patient population.
CONCLUSION: The use of dapagliflozin in addition to standard therapy for the treatment of comorbid patients with CHF and type 2 diabetes is clinically and economically feasible, considering the cost per year of life saved, adjusted for quality of life.
Review
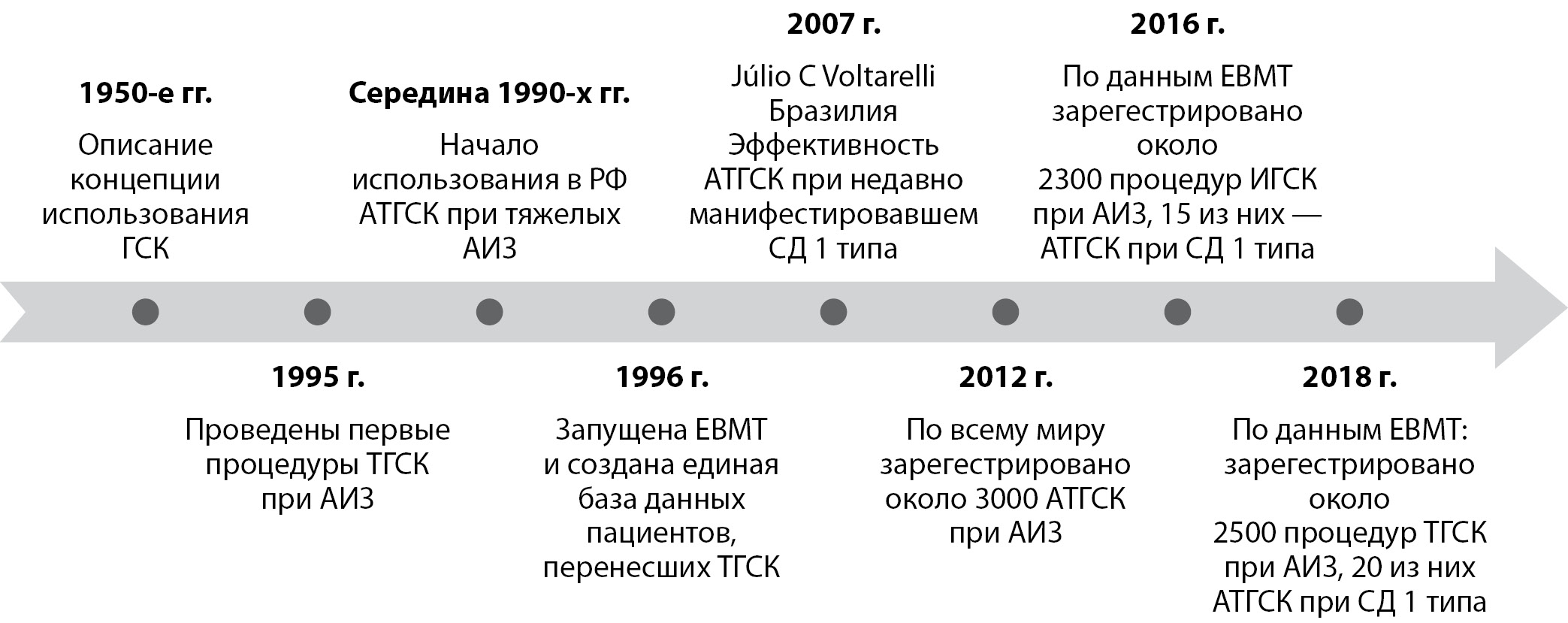
Type 1 diabetes mellitus (DM) is one of the most common autoimmune disease that is treated with lifelong insulin therapy. Non-target indicators of glycemic control, which are observed in 71% of patients, lead to the formation and progression of diabetes complications, early disability and mortality. In this regard, the search for new approaches to the treatment and prevention of type 1 DM seems to be relevant. Various methods of immunological prophylaxis for the development of type 1 DM have been studied, in particular, the use of monoclonal antibodies. Thus, in November 2022, teplizumab was approved to slow down the clinical progression of the stage of type 1 DM. The prospects for the use of new options for islet cell transplantation are being studied — in June 2023, an allogeneic donor β-cell transplant obtained from the pancreas of donors after death was approved. Another pathogenetically substantiated method for the prevention and treatment of autoimmune diseases is high-dose immunosuppressive therapy with autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HDIT-HSCT). HDIT-HSCT demonstrated its effectiveness and cost-effectiveness in various clinical trials. This review provides up-to-date information on modern methods of immunological prophylaxis of type 1 DM.
Case report
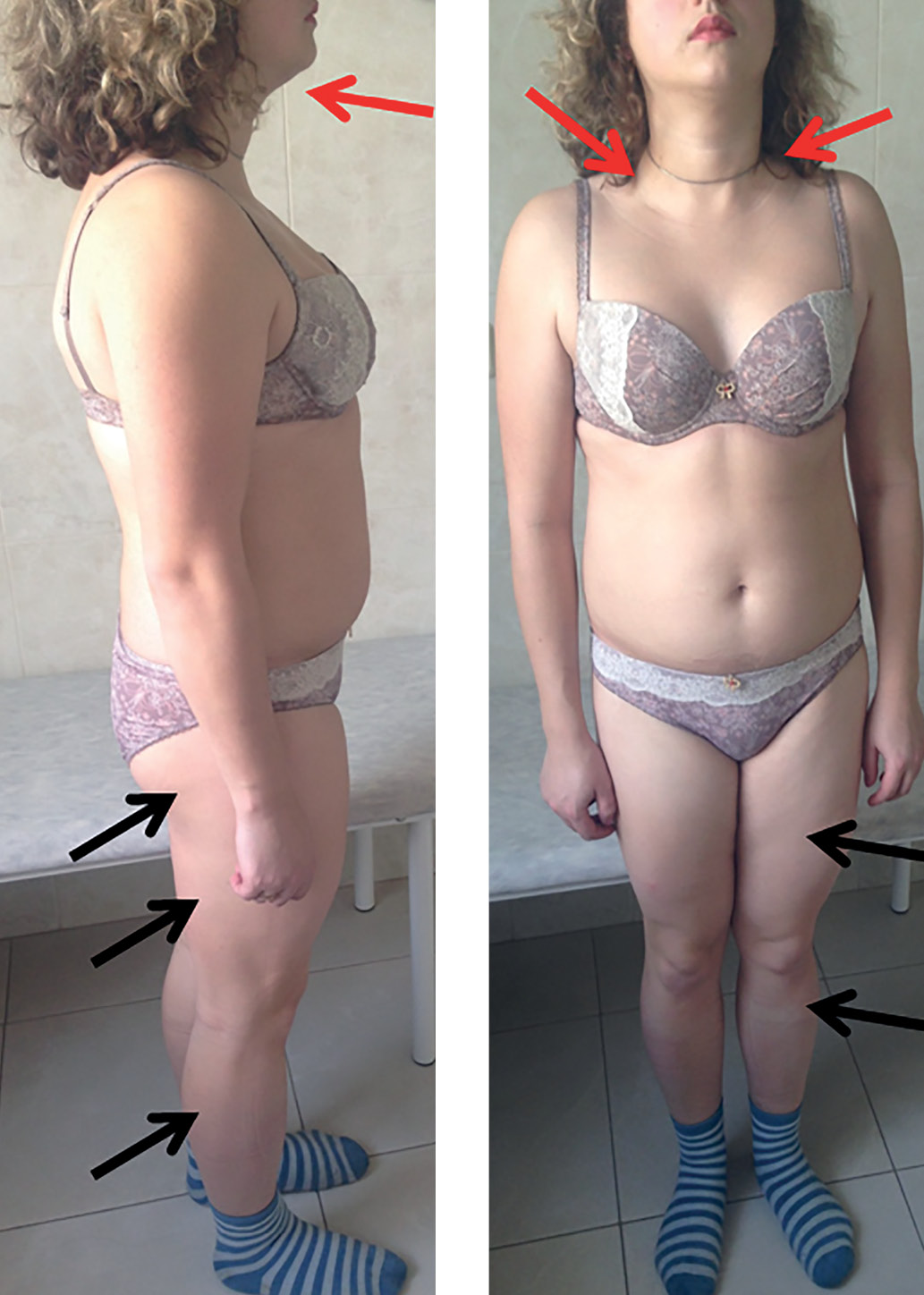
Lipodystrophy syndromes are a heterogeneous group of extremely rare, inherited or acquired disorders that are characterized by total or partial fat loss or its improper redistribution. The prevalence of lipodystrophies is estimated to be 1:1,000,000 in the population, with approximately 1,000 cases currently described in the literature.
Sarcoidosis is a multisystem disease of unknown etiology that is characterized by the formation of non-caseating epithelioid granulomas in the affected tissues. Despite the large number of studies, the etiology and pathogenesis of sarcoidosis still remain unknown. Most researchers allude to the possible autoimmune or immune-mediated genesis of the disease.
This article presents a series of unique clinical cases of a combination of two rare diseases in one patient: sarcoidosis and familial partial lipodystrophy.
Diabetes mellitus type 1 (DM1) and chronic adrenal insufficiency (CAF) are among the most common autoimmune endocrine diseases that develop both isolated and in combination with each other and with other diseases of autoimmune origin, as part of various syndromes. At the same time, type 1 diabetes is quite often the first component of a systemic autoimmune lesion and acts as a predictor of the development of congenital disorder, which, in turn, against the background of type 1 diabetes, acquires a mild, sometimes atypical course, which complicates the diagnosis and prescription of therapy. The clinical case describes a patient with type 1 diabetes and end-stage chronic kidney disease (CKD), kidney allotransplantation (ART), who was on triple immunosuppressive therapy, who developed CHN, which was manifested by severe hyponatremia and the occurrence of frequent hypoglycemic conditions.
News
Due to its effect on insulin resistance, ease of administration and favorable safety profile, metformin has been included in the recommendations of foreign medical communities for the management of pregnant women with hyperglycemia since 2008. However, in Russia, the use of any oral hypoglycemic agents during pregnancy is still contraindicated. However, recent studies demonstrate the safety and positive effects of metformin on pregnancy in patients with pregestational diabetes mellitus, polycystic ovary syndrome and gestational diabetes mellitus. In 2023, the Federal Service for Surveillance in Healthcare of the Ministry of Health of Russia updated the instructions for the medical use of Glucophage® and Glucophage®Long: pregnancy was excluded from the “Contraindications” section and moved to the “With caution” section. This resolution is intended to evaluate studies of the effectiveness and safety of metformin, as well as to study the experience of foreign colleagues and Russian legal aspects of prescribing metformin in the stages of preparation for pregnancy, during it and in the post-gravid period.
On March 20, 2024, an interdisciplinary meeting of the Expert Council on the current problem of B12 insufficiency/deficiency and the prevalence of this condition among endocrine patients was held at the Endocrinology Research Centre (Moscow). The purpose of the meeting was to assess the role of B12 deficiency in reducing the quality of life of patients of different groups and to outline a strategy for the management of patients with vitamin B12 insufficiency/deficiency by endocrinologists.
The resolution of the expert council was developed by leading specialists in various specialties.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0).
ISSN 2072-0378 (Online)