Original Studies
BACKGROUND: Patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1D) have an earlier age of onset and a longer course of the disease, already by middle age they have the development of microand macrovascular diabetic complications that reduce the quality and duration of life.
AIM: To evaluate the prevalence of chronic kidney disease (CKD) and other late complications of T1D depending on renal dysfunction in the population of patients with T1D with disease duration of 20 and more years, who underwent examination and treatment in Endocrinology Research Centre.
MATERIALS AND METHODS: A one-stage single-center epidemiological non-randomised study was conducted using the database of Endocrinology Research Centre with the study of 500 patients’medical histories with long-term T1D (20 years and mores), without kidney damage and with CKD at different stages (CKD C1–C5, C5D, after transplantation), examined and treated from 2011 to 2023.
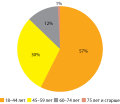
RESULTS: Normal renal function was observed in 10.8% of patients (n=54). Terminal stage of CKD was reached in 28.0% (n=140), of which 12.4% were on renal replacement therapy with program hemodialysis (RRT-HD), and 12.0% after isolated kidney transplantation or combined kidney and pancreas transplantation, the rest were at different stages of CKD. Normoalbuminuria was observed in 15.4% (n=77) among 500 patients. The prevalence of late complications of DM among the examined patients was high and increasing with the progression of renal dysfunction: diabetic retinopathy was diagnosed in 96% of patients, distal symmetrical polyneuropathy — in 97% of patients, various forms of autonomic neuropathy — in more than half of patients. About 60% of patients had diagnosed arterial atherosclerosis in the legs, about one third — atherosclerosis of brachiocephalic arteries, 23% — confirmed coronary heart disease, and suffered cardiovascular events (myocardial infarction, acute cerebral circulation disorder) — 19% of patients, about half of whom had CKD of different severity. Factors for increased risk of cardiovascular disease: estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR)<60 mL/min/1.73m2, OR=7.1; 95% CI 3.6–8.4; p<0.001), eGFR <30 mL/min/1.73m2 OR=8.7; 95% CI 2.8–8.4; p<0.001), eGFR <15 mL/min/1.73m2 OR=14; 95% CI 6.3–31.3; p<0.001); albuminuria > 30 mg/g OR=2.4; 95% CI 1.6–3.6; p<0.001), dialysis OR=14.1; 95% CI 6.2–32.1; p<0.001), kidney transplant OR=11.7; 95% CI 5.4–24.9; p<0.001). Manifestation of T1D between 1996–2002 reduced the risk of developing CKD by 10.75; 95% CI 4.37; 27.03) vs manifestation of T1D earlier. Age of T1D debut 6–17 years increased the risk of reaching terminal CKD vs age of debut >18 years: OR=2.4; 95% CI 1.22; 5.022; p=0.012).
CONCLUSION: Despite a significant reduction in the risk of developing CKD in individuals with T1D debut between 1996 and 2002, renal dysfunction is a frequent complication in patients with a long disease course, combining with other late complications and contributing to a high risk of terminal stage of CKD and cardiovascular events. Early age of T1D debut increases the risk of terminal CKD.
BACKGROUND. Glucose metabolism disorders (GMD) were detected both in acute and in post-COVID, however, its pathogenic aspects remain unclear.
AIM. To analyze the occurrence of GMD in post-COVID patients who have had moderate and severe COVID-19 without previously known GMD disorders, and evaluate expression of SARS-CoV-2 proteins and its entry factors in pancreas in acute COVID-19.
METHODS. Among 187 hospitalized patients with confirmed COVID-19 141 patients without previously diagnosed GMD underwent follow-up post-COVID visits. The examination for all patients included anthropometric measurement with calculation of BMI, level of HbA1c and fasting plasma glucose, for 106 patients level of insulin and HOMA-IR index was analyzed. For histological examination, pancreas fragments of 20 patients with fatal outcome were selected. Immunohistochemical study was performed with antibodies to SARS-CoV-2, ACE2, DPP4, as well as double-labeled immunofluorescence microscopy (insulin-SARS-CoV-2, insulin-ACE2, insulin-DPP4).
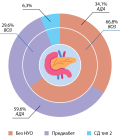
RESULTS. Among 141 patients in post-COVID period, 9 (6.3%) had HbA1c or fasting plasma glucose levels that met criteria for diabetes mellitus, 38 (26.9%) — exceeded normal values (WHO), and 84 (59.6%) had GMD according to criteria of the ADA. In post-COVID, patients with GMD had a higher BMI and HOMA-IR index (p=0.001) compared to patients with normal glycemic levels. Only 40.4% of people had HOMA-IR index above 2.7. Patients with GMD had higher level of CRP (p=0.007) and a maximum glucose level (p=0.019) in the acute period. Positive relationship was found between BMI and HOMA index both in acute (p<0.001; r=0.389) and post-COVID (p<0.001; r=0.412) periods, as well as the level of HbA1c in acute period (p=0.019, r=0.202) and in post-COVID (p=0.004, r=0.242).
Histological and immunohistochemical studies showed the expression of SARS-CoV-2 proteins in 1.85% [0–15.4] and 11.1% [5.3–14.8] cells of the Langerhans islets in patients who died on the second and third waves, respectively. The expression of ACE2 and DPP4 in the islets of Langerhans did not exceed 0.4% [0–1.7] and 0.5% [0–0.8] of cells, respectively. Double-labeled immunofluorescence microscopy showed co-localization of SARS-CoV-2, ACE2, DPP4 with insulin.
CONCLUSION. Post-COVID Glucose metabolism disorders may be explained by direct cytotoxic effect of SARS-COV-2, increased glucose toxicity and insulin resistance because of the acute infection and its complex therapy.
© Fatima O. Ushanova1*, Tatiana Y. Demidova1, Tatiana N. Korotkova2
1Pirogov Russian National Research Medical University, Moscow, Russia
2Federal Research Centre of Nutrition, Biotechnology and Food Safety, Moscow, Russia
BACKGROUND: The prevalence of gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) is growing rapidly, along with which the typical portrait of a pregnant woman with this disease is changing. Frequent detection of GDM in the early stages of pregnancy causes a high interest in the study of new mechanisms of its development.
AIM: Evaluation of the state of the incretin response based on the analysis of the secretion of GLP-1, glucagon, insulin and c-peptide in pregnant women with different periods of GDM development.
MATERIALS AND METHODS: A single-center prospective comparative uncontrolled study that included pregnant women with GSD, divided into 2 groups depending on the duration of the disease: group 1 — pregnant women who were diagnosed at <24 weeks of gestation (n=65), group 2 — at ≥24 weeks of gestation (n=26). All patients underwent a set of diagnostic measures, including a stress test with the determination of GLP-1, glucagon, insulin, c-peptide before and after a mixed breakfast, and an assessment of insulin resistance. Glucose monitoring was performed for pregnant women with GSD using the FreeStyle Libre Flash system (Abbott Diabetes Care Ltd., UK).
RESULTS: The total number of subjects was 91. The average age was 32.05±5.6 (95% CI 30.9; 33.2) years. Pregnant women of both groups were comparable in age, body weight and glycemic level at the time of diagnosis. The basal blood insulin level in the general group was 7.2 [4.9; 12.1] µme/ml, C-peptide — 1.5 [1.17; 2.24] ng/m, glucagon — 70.1 [56.2; 100] pg/ml, GLP-1 — 1.16 [0.94; 1.22] ng/ml. In 31% For women, the HOMA-IR index was ≥2.7. The basal level of glucagon was significantly higher in the group of early development of GSD: 70.9 [57.7; 109.2] pg/ml versus 61.7 [46.6; 87] pg/ml, p=0.04. In both groups of pregnant women, the decrease in glucagon secretion was not statistically significant, most had a paradoxical increase in glucagon secretion. When assessing the dynamics of GPP-1, a significant increase in the indicator was detected only in the 1st group: Δ GPP-1 0.15 [-0.07; 0.96], p <0.01. In the second, the dynamics of the indicator was not statistically significant (p=0.211). Negative correlation of the increase in GLP-1 with MAGE (r=-0.34, p<0.05), glycemic lability index LI (r=-0.4, p<0.05) and J-index (r=0.44, p<0.05) was revealed.
CONCLUSION: The preservation of the physiological secretion of insulin and c-peptide in the form of a satisfactory increase in indicators after a food load was established. A violation of postprandial suppression of glucagon secretion was revealed. The increase in GPP-1 in response to food loading was disrupted in the case of the development of GSD during pregnancy ≥ 24 weeks.
BACKGROUND. The search for new effective methods of treatment and prevention of COVID-19 in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) remains an urgent task for the healthcare system.
AIM. To evaluate the efficacy and safety of initiating of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1RA) therapy in T2DM patients hospitalized with COVID-19.
MATERIALS AND METHODS. The inclusion criteria were history of T2DM, BMI> 27 kg/m2, confirmed diagnosis of COVID-19. The intervention group of 53 patients started dulaglutide therapy (1,5 mg once weekly) during the first 24 hours of admission, the control group consisted of 50 patients, who proceeded with glucose-lowering therapy. We evaluated the effect of therapy on carbohydrate metabolism, laboratory and clinical parameters, the outcome of COVID-19 and the safety of therapy (hypoglycemic events, side effects).
RESULTS. There were no differences found in the degree of decrease in the level of glycemia in the compared groups: fasting plasma glucose (FPG) on day 7 of hospitalization– 8,2 [6,0;9,8] mmol/L vs 8,1 [6,5;9,8] mmol/L (p=0,935), mean daily glycemia (MDG) — 9,7 [8,3;11,8] mmol/L vs 11,1 [8,7;12,8] mmol/L (p=0,182). Therapy of dulaglutide had a positive effect on inflammatory markers: CRP (15,8 vs 24,4 mg/l, p=0,035), LDH (261,6 vs 326,1 U/l, p=0,016) and the level of lymphocytes (1,2 vs 0,9 x 10*9/L, p=0,049) and on clinical parameters: saturation, the need for oxygen therapy and the risk of severe course according to the NEWS2 scale. The death rate in the group receiving GLP-1RA is 3,5 times lower compared to the control group (5,7% vs 20,0%, p=0,038). The initiation of dulaglutide therapy in patients with T2DM hospitalized with COVID-19 reduced the chance of death and transfer to mechanical ventilation by 4,2 times compared to the control group (OR = 0,24, 95% CI: 0,062–0,931). GLP-1RA therapy in patients with COVID-19 and T2DM is safe in terms of hypoglycemic events and side effects.
CONCLUSIONS. The initiation of GLP-1RA therapy leads to a decrease in FPG and MDG, comparable with the control group. The start of GLP-1RA therapy in hospitalized patients with COVID-19 and T2DM reduces the chance of death, favorably affecting on laboratory and clinical parameters.
BACKGROUND: Diabetic neuroosteoarthropathy is a severe and insufficiently studied complication of diabetes mellitus, which is characterized by progressive destruction of bones and joints against the background of neuropathy and leads to the formation of foot deformities of varying severity. The search for predictors of this pathology is extremely relevant, because will optimize therapy and reduce the risk of limb amputation.
AIM: To compare the levels of advanced glycation end products and their receptors in the blood and bone tissue in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and diabetic neuroosteoarthropathy and in individuals without this complication in order to determine the possibility of using these parameters as early predictors of severe foot deformities in this category of patients.
MATERIALS AND METHODS: During hospitalization for planned surgical treatment, venous blood and bone tissue samples were taken from patients with chronic (inactive) stage of DNOAP and patients with neuropathic foot ulcers.
RESULTS: The study included 88 patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and neuropathic form of diabetic foot syndrome, who were divided into 2 groups. Group 1 consisted of patients with chronic diabetic neuroosteoarthropathy, group 2 — patients with severe diabetic neuropathy without osteoarticular disorders. The study did not show statistically significant differences in the level of AGE in the blood serum of patients with DNOAP and without this complication, however, a significant increase in AGE receptors (RAGE) in bone tissue was recorded in the group of patients with DNOAP compared with the control. Patients with increased RAGE expression in bone had higher blood levels of AGE compared to the group without this complication, but this difference was not significant.
CONCLUSION: For the first time, a study of AGEs and receptors for them in the blood serum and bone tissue in individuals with DNOAP and without this complication was carried out. The obtained results suggest that the determining factor in the rate of formation and the likelihood of recurrence of DNOAP in type 2 diabetes mellitus is not the content of AGEs in the blood, but the expression of their receptors in bone tissue.
BACKGROUND: The risk of acute myocardial infarction (AMI) in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is 2 times higher than without DM. Previously an association between the time in the target range of glycemia during hospitalization of AMI in patients with T2DM (hTIR — «hospital time in range») and long-term prognosis was found. It is supposed that a differentiated approach to glycemic management will help to achieve a higher level of hTIR and will lead to an improved prognosis.
AIM: To evaluate the effectiveness of differentiated approach to glycemic management in patients with T2DM during inpatient treatment of AMI and impact on long-term prognosis.
MATERIALS AND METHODS: The study included patients with T2DM who were hospitalized with AMI with ST-segment elevation and underwent percutaneous coronary intervention. A total amount of patients was 161; 102 were in the main group, 59 in the control group. There was a differentiated approach to glycemia management based on phenotype determination in the main group. Insulin therapy was prescribed to patients with the 1st phenotype during the entire inpatient treatment. Patients with the second phenotype received insulin therapy followed by switching oral antidiabetic drugs (OAD). Patients of the 3rd phenotype were prescribed only OAD. In the control group, therapy of T2DM was prescribed according to the standard hospital procedures based on current clinical recommendations.
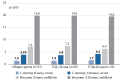
RESULTS: In the main group, 22 patients (22%) were in the 1st phenotype, 54 (53%) –in the 2nd, 26 (25%) –in the 3rd. The average glycemia during hospitalization in the main group was lower than in the control group: 9.4±1.7 mmol/l vs 10.3±2.3 mmol/l (p=0.006). The hTIR in the main group was 58 [53; 71]% vs 46 [33; 63]% in the control group (p<0.001). It was shown that when hTIR > 55% is reached, the risk of cardiovascular death within a year after hospitalization is reduced by 80%.
CONCLUSION: The differentiated approach to glycemic management in patients with T2DM leads to an improvement in glycemic control during inpatient treatment of AMI and is accompanied by a tendency to a lower incidence of cardiovascular death within a year after hospitalization. Achieving hTIR > 55% is associated with a multifold reduction of the risk of cardiovascular death in a year. About 25% of patients with DM2 during inpatient treatment of AMI do not need the insulin therapy.
Review
In 1838 G. Rees, a doctor from London (Guy's Hospital), for the first time isolated excess sugar from the blood serum of a patient with diabetes mellitus. Diagnosis of diabetes mellitus gradually developed. The next step was the understanding that regular monitoring of glucose levels by the patient himself is an integral part of diabetes mellitus therapy. The starting point of the technology for self-monitoring of diabetes mellitus was the determination of the sugar content in urine using chemical reactions. The method had no great clinical significance, it only indicated a progressive disease. The first Dextrostix blood glucose test strip (Ames-Mile's laboratories) was introduced in 1964. In 1970, the first automated blood glucose analysis system, the Ames Reflectance Meter (ARM), was created. Over time, the technology has been improved, accuracy, visibility, comfort, and an individual approach to glucometry have been formed. A new chapter was the development of remote technologies and the possibility of remote monitoring. More advanced data processing is now available in tabular and graphical form, with the calculation of 7-, 14-, 30-, and 90-day average glycemic values. A promising direction is the introduction of artificial intelligence in the management of diabetes mellitus.
The incidence of diabetes is increasing in all age groups. The use of technological devices for the treatment of diabetes, such as continuous glucose monitoring (CGM), is expanding and is associated with improved control of blood glucose levels in order to prevent complications of this disease. Reducing glycemic variability and maintaining optimal glycemic control is critical to the management of patients with type 1 diabetes. The usefulness of glycemic monitoring devices has also been shown for patients with type 2 diabetes. CGM technology is constantly being improved in terms of analytical performance, biocompatibility, wear duration, safety and clinical performance. However, commonly used minimally invasive CGMs do not measure blood glucose directly, but instead measure the glucose concentration in the interstitial fluid (IF), so changes in IF glucose occur with a delay of 5 to 15 minutes compared to blood glucose. In addition, the lifetime of minimally invasive CGM sensors is relatively short, up to 14 days. Therefore, the introduction into clinical practice of devices for non-invasive glucose measurement in people with diabetes, which overcome the above-mentioned limitations of minimally invasive CGM, will expand the possibilities of glucose monitoring among patients with diabetes. The purpose of this review was to present the technologies of CGM system sensors approved for medical use in Russia and other countries.
Metformin, known in the medical community as the drug of first choice for type 2 diabetes mellitus, belongs to the group of biguanides and has proven to be an effective treatment in clinical practice. Our knowledge of the pharmacodynamic properties of metformin has long been limited to the following well-known mechanisms: a decrease in hyperglycemia due to an increase in peripheral insulin sensitivity, glucose utilization by cells, inhibition of hepatic gluconeogenesis, an increase in the capacity of all types of membrane glucose transporters, activation of fibrinolysis, and a decrease in the levels of atherogenic lipoproteins. Recent studies show that the range of positive pleiotropic effects of metformin is not limited to the above, and that the molecular mechanisms of its action are more complex than previously thought. This article presents a less known, but equally important action of metformin, in particular, its anti-oncogenic, antiviral, and anti-aging effects. In our study, we highlight that the activation of 5’-adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase (AMPK) should be considered as the primary mechanism of action through which almost all beneficial effects are achieved. In the light of recent scientific advances in metformin pharmacology, together with the pathogenetic uncertainty of the term «biguanide», it seems fair and reasonable to apply a more relevant definition to the drugn, namely «AMPK activator».
Gliflozins are a relatively new class of oral antihyperglycemic drugs that are increasingly being introduced into routine practice in the treatment of patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (DM2). The hypoglycemic effect of gliflozins is associated with the stimulation of glucosuria, however, in addition to a pronounced hypoglycemic effect and high safety, these drugs also have many pleiotropic properties, due to the presence of many direct and indirect points of application. The purpose of this paper is to provide an overview of the currently best studied neuroprotective effects of this class of drugs. As materials in the course of the work, studies of foreign colleagues published in the period 2008–2022 were used. Analysis of the works showed that the neuroprotective effect of gliflozins is associated with many different mechanisms. Thus, gliflozins realize an anti-inflammatory effect by activating the M2 subpopulation of macrophages, reducing pro-inflammatory neurotransmitters (related primarily to the inflammasome). In addition, by reducing the activity of the mTOR signaling pathway, the drugs reduce the amount of beta-amyloid and improve neurotransmission. A group of works also showed the antiacetylcholinesterase effect of gliflozins, not to mention the decrease in the intensity of non-enzymatic protein glycation and insulin resistance. All of the above mechanisms provide an anti-inflammatory, anti-atherogenic effect, improve cognitive abilities in patients, reduce the frequency of hemorrhagic stroke, and can also potentially improve prognosis in patients with Alzheimer’s disease (AD). The effects described above were obtained during preclinical trials and many experimental studies, and some effects have already demonstrated their consistency in prospective clinical trials. However, the data obtained are still insufficient to form clear indications for this class of drugs in neurology, so the topic requires further study and clinical trials.
Patients with diabetes mellitus and renal pathology are at high risk of developing end-stage kidney disease (ESKD) and cardiovascular disease (CVD), including atrial fibrillation as an life-threatening condition. The intense annual increase in patients with diabetes mellitus, mainly due to the patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2D), and diabetic nephropathy sets a new goal for researchers to expand the range of drugs with cardio- and nephroprotective effects to offset the residual risks of development and progression of chronic kidney disease (CKD) and CVD in this cohort of patients. One of such drugs is finerenone — a novel selective non-steroidal mineralocorticoid receptor (MR) antagonist (MRA), hyperactivation of which mediates renal inflammation and fibrosis, cardiac remodeling and changes in its structural and electrical characteristics. This review presents the results of the sub-analysis of FIDELIO devoted to the mechanism of drug action, the finerenone efficacy evaluation, its comparison with the efficacy of sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors and glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists with already proven organoprotective properties with respect to reducing the risk of renal and cardiovascular endpoints.
Short Messages
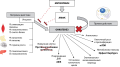
Open source closed loop automated insulin delivery (CL-AID) systems are increasingly used in the treatment of diabetes. Not being officially approved, such systems are used by patients on their own initiative. Accordingly, the medical community has very little information about the treatment satisfaction and needs of patients that use these systems. We conducted an anonymous internet survey of Russian users of open source CL-AID systems. Ninety-five respondents reported using AndroidAPS (60%), FreeAPS X (16.6%), Loop (10.5%), FreeAPS (5.3%), OpenAPS (3.2%), and Omnia (2.1%). The duration of use of the systems ranged from 0.1 to 6 years (median 2.1 years). The mean HbA1c in users was 6.1% v.s. 7.3% on previous therapy. Most respondents reported an increase in Time in Range (88%), a decrease in the number of hypoglycemic episodes (73%), an improvement in the sleep quality (76%), general well-being (73%), social adaptation (56%) and self-confidence (69%), as well as a decrease in stress levels (56%) after switching to the systems. Ninety (94%) survey participants reported increase in the treatment satisfaction. The majority of respondents (68%) consider themselves advanced gadget users. However, 79% of them had technical difficulties when setting up the system for the first time, 46% had difficulty understanding the settings of the algorithm / program, and 35% spent a lot of effort studying the system. Support from the attending physician was reported by 27% of respondents, 35% noted the neutral attitude to the use of the system, and in 18% of cases the doctor was not aware of its use. All respondents, with the exception of two who found it difficult to answer, plan to continue using the system. Thus, from the patient's point of view, open source CL-AID systems have a positive effect on glycemic control and quality of life. The medical community should pay more attention to the needs of patients using these systems in treatment.
News
TThe annual increase in the prevalence of type 2 diabetes mellitus emphasizes the relevance of the search for new treatment options, along with necessity for regular review of proven therapeutic solutions. Today, dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors (DPP-4i, gliptins) are effective and safe hypoglycemic therapy, which is included in modern standards of treatment of type 2 diabetes. In 2022, the availability of this group of drugs for Russian patients has significantly increased. This circumstance became a prerequisite for holding a National Council of Experts with the participation of members of the Russian Association of Endocrinologists. The task of the Council was to determine the place of DPP-4i in the treatment of patients with type 2 diabetes in 2023. During the meeting of the Council, experts summarized the evidence base of DPP-4i taking into account the latest scientific data and determined the optimal clinical portraits of patients for the use of DPP-4i in accordance with updated national recommendations.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0).
ISSN 2072-0378 (Online)