Original Studies
BACKGROUND: Population aging leads to an increase in the prevalence of age-associated diseases, which makes it relevant to study the characteristics of diabetes mellitus (DM) in older adults.
AIM: The aim of our study was to analyze the clinical and epidemiological characteristics of DM in elderly people (≥65 years), the state of carbohydrate metabolism (level of HbA1c), the frequency of diabetic complications and the characteristics of glucose-lowering therapy (GLT) in the Russian Federation (RF).
MATERIALS AND METHODS: Object of the study: Russian cohort of patients with diabetes based on the depersonalized "Database of clinical and epidemiological monitoring of DM in the territory of the RF", certificate of state registration database №2020622447 (http://diaregistry.ru, register of DM), including patients from 87 regions of the RF, n=5205647. Patients were stratified by age ≥ and <65 years into 2 groups: “65+”, n=3085805 and “65-”, n=2119842 and analyzed in the subgroups of type 1 and type 2 DM, in dynamics 2013–2023.
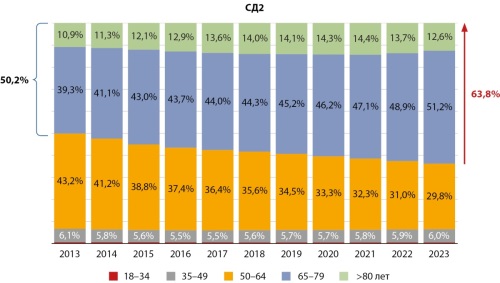
RESULTS: The total number of DM patients aged 65+ is 3085805, which is 59,3% of the total number of DM patients; with type 2 diabetes (T2DM) — 63,8%, with type 1 diabetes (T1DM) — 8,1% of patients. Over the period 2013-2023, there was an increase in the proportion of elderly people with T2DM from 50,2% to 63,8%, with T1DM — 7,9-8,1%. The proportion of patients with onset of T2DM over the age 60 years increased from 51% to 63%. Clinical characteristics in the «65+» and «65-» group differed significantly in T1DM in the level of HbA1c 7,8 vs 8,0%, level of GFR 75,0 vs 107,2 ml/min/1,73 m2, BMI 26,9 vs 23,2 kg/m2; in T2DM the level of HbA1c 7,3 vs 7,5%, level of GFR 73,1 vs 89,1 ml/min/1,73 m2; BMI 30,9 vs 32,0 kg/m2, respectively. The proportion of obese patients increased with age in T1DM from 13% to 36%, and decreased in T2DM from 62% to 54%. In the group of older patients with both types of DM, a higher frequency of diabetic complications with combined damage to target organs of CKD, ASCVD and CHF was observed: on average 4,6 times with in T1DM, 2,2 times in T2DM. When analyzing the GLT in the group of 65+, sulfonylurea (SU) drugs dominate 45,3% vs 35,0%, the proportion of metformin and drugs with organoprotective effects (DPP-4 inhibitors, SGLT-2 inhibitors, arGLP-1) decreases.
CONCLUSION: An analysis of older patients from the all-Russian population of DM patients showed significant clinical differences characterizing the pathophysiological features of the course of DM in the elderly, which requires special attention to the aspects of individualization of treatment goals and choice of therapy from the standpoint of safety and risk reduction in this cohort of patients.
BACKGROUND: Familial clustering of type 1 diabetes (T1D) highlights the importance of genetic and environmental factors in the pathophysiology of diabetes mellitus (DM). It could be the key to understanding of new immunological and genetic characteristics of T1D.
AIM: To study the clinical, biochemical, immunological and genetic characteristics of children with familial forms of T1D.
MATERIALS AND METHODS: A single-center cross-sectional study included 267 patients with familial T1D and 681 patients with sporadic T1D. Clinical and metabolic characteristics, beta cell autoantibodies and HLA class II genetics from patients with T1D hospitalized to Endocrinology Research Centre Moscow between 2016 and 2023 were analyzed.
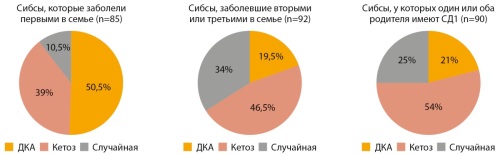
RESULTS: The median age of onset of DM was significantly lower in children with familial T1D (5,2 [3,0; 8,0] vs 6,4 [3,6; 9,2], p<0,001). Children with sporadic T1D had diabetic ketosis or diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) at presentation more frequently (90,3% vs 74%, p<0,001). Among the sib-pair groups 50,5% of first-affected siblings and 19,5% of second- and third-affected siblings had DKA at presentation, while in children from parent-offspring subgroup DKA episodes were observed in 21% of patients (p<0,001). IAA and GAD antibodies were more frequent in familial cases (p<0,013, p<0,003). In our groups, no significant differences in metabolic compensation of the T1D were found. HLA haplotypes associated with an increased disease risk DRB1*04-DQA1*03:03-DQB1*03:02 and DRB1*07-DQA1*02:01-DQB1*02:02 were more common in children with familial T1D (p<0.001 and p<0.001), while the protective haplotype DRB1*08-DQA1*04:01-DQB1*04:02 was more frequent in sporadic forms.
CONCLUSION: Due to our study familial forms of T1D are characterized by an earlier age of onset, a smaller risk of DKA at presentation, as well as features of the immunological profile and predisposing and protective HLA haplotypes presentation. We believe more studies are required in the future to look for risk factors and pathogenesis unserstanding.
BACKGROUND: The prevalence of overweight and obesity in patients with type 1 diabetes (T1D) is increasing, which raises the issue of their impact on the development of complications.
AIM: to study the associations of overweight and obesity with vascular complications, cardiovascular risk factors and serum levels of vascular remodeling biomarkers in patients with T1D.
MATERIALS AND METHODS: The study included 547 patients, including 309 with body mass index (BMI) <25 kg/m2, 155 with BMI 25–29.9 kg/m2, and 83 with BMI ≥30 kg/m2. Insulin sensitivity was assessed by the estimated glucose disposal rate. In the serum of 130 patients and 30 individuals with normal weight and normal glucose tolerance, concentrations of advanced glycation end products (AGEs), endothelin-1, endothelial NO synthase (NOS3), adrenomedullin (ADM), endothelial cell-specific molecule-1 (ESM1), cell adhesion molecules (ICAM-1 and VCAM-1), integrin-associated protein-1 (IAP-1), integrin receptor subunit (ITGB1), heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1), GAS6, decorin, and transforming growth factor β1 (TGF-β1) were determined by ELISA.
RESULTS: Obesity in patients with T1D was independently associated with coronary artery disease, myocardial infarction, and chronic heart failure. Overweight was an independent predictor of chronic heart failure only. Patients with BMI ≥25 kg/m2, when compared with those with BMI <25 kg/m2, were older, had a reduced insulin sensitivity and increased levels of triglycerides, LDL-cholesterol, uric acid, and high-sensitivity C-reactive protein. Patients with T1D, as compared with controls, showed a significant increase in serum AGEs, endothelin-1, ICAM-1, VCAM-1, IAP-1, ESM1, HO-1, GAS6, and TGF-β1. Overweight patients, when compared with those with BMI <25 kg/m2, demonstrated higher levels of ICAM-1, IAP-1, ITGB1 and TGF-β1, while obese individuals had increased concentrations of AGEs, IAP-1 and HO-1.
CONCLUSION: In patients with T1D, overweight and obesity are associated with vascular complications, their risk factors and biomarkers of vascular remodeling.
AIM. To study the effect of the non-calorie sweetener erythritol and the combination of erythritol and sucrose on postprandial secretion of insulin and peptide-YY (PYY).
MATERIALS AND METHODS. A comparative study was conducted to assess the effect of erythritol, sucrose and a combination of erythritol and sucrose on postprandial glucose, IRI and PYY levels. The participants were selected from among healthy volunteers, aged 18 to 35 years. If the participants met the selection criteria, further stages of the study were carried out. During the study, each participant took a solution of sucrose 75 g, erythritol 75 g or a mixture of sucrose and erythritol (75 g and 25 g, respectively). Further determination of glucose and insulin was carried out every 30 minutes, so glucose, insulin and PYY values were determined initially and at the 30th, 60th, 90th and 120th minutes.
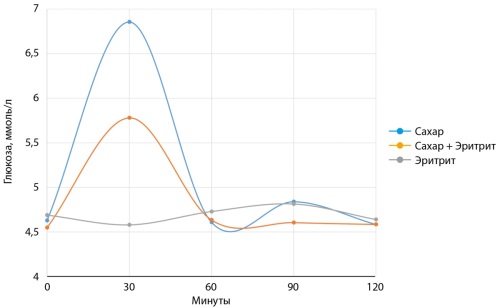
RESULTS. Data were obtained confirming the absence of the effect of erythritol on postprandial secretion of insulin and glucose. In our work, we also demonstrated a decrease in postprandial glycemia when taking sucrose and erythritol together. Sucrose and erythritol equally stimulated PYY secretion.
CONCLUSION. Our data show that erythritol can be considered as an optimal sugar substitute in people with impaired carbohydrate metabolism and obesity.
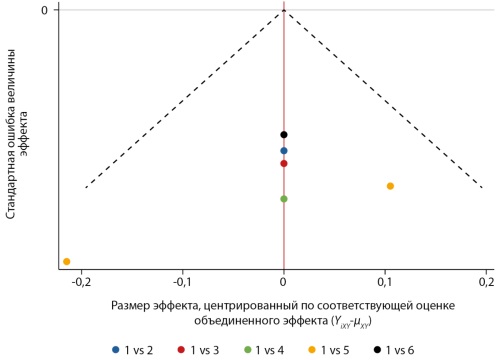
The increase in the number of patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2D) and mortality among them forces us to look for ways to optimize T2D treatment. At the same time, more than half of patients with an established diagnosis do not reach the glycemic targets and require intensification of therapy. Due to the progressive deterioration of the glycemic status, almost one in five T2D patients requires insulin therapy (IT), and over time, IT intensification with titration of the dose of insulin. This approach is limited by a few adverse effects such as: an increased risk of severe hypoglycemia, weight gain, decreased sodium excretion, which means fluid retention in the body, and the patient’s unwillingness to carry out complex therapy regimens. The addition of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2i) inhibitor with an insulin–independent mechanism of action to the treatment is aimed to solve the problem of optimizing glycemic control in this category of T2D patients. The purpose of this network meta-analysis (NMA) was to indirectly compare the efficacy and safety of SGLT2 inhibitors added on top of insulin in T2D patients. The analysis included randomized clinical trials in which dapagliflozin, empagliflozin, ipragliflozin, luseogliflozin, and ertugliflozin were prescribed as SGLT2i. The primary endpoint was a change in glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c), and the secondary endpoints were changes in a mean of fasting plasma glucose, body weight and blood pressure, as well as the mean change in daily dose of insulin. The analysis of safety data included a comparative assessment of the incidence of hypoglycemia, reproductive tract and urogenital infections, and hypovolemia. The results of the conducted NMA demonstrate the comparable effectiveness of various SGLT2i regarding managing of glycemic status in T2D patients receiving insulin, along with commensurate safety and tolerability of therapy.
BACKGROUND: Despite existing recommendations for the initial calculation of insulin pump settings, the process is largely subjective and depends on the physician’s personal experience.
AIM: Development of a clinical decision support system (CDSS) that determines the initial settings of the insulin pump, which would have satisfactory agreement with the expert opinion of physicians.
MATERIALS AND METHODS: Neural network model developed using data (continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion (CSII) settings, age, weight, total daily dose, and HbA1c) from 2850 children with T1D who were switched to CSII and achieved optimal glycemic control according to glucose levels. CDSS utilizing the model implemented as a computer program in Python.
A prospective assessment of the agreement between the recommendations of the CDSS and the physician conducted on 35 data sets of children with T1D (median age 9.3 years [6.4, 11.5]), and 840 points for decisions were analyzed. 4 degrees of agreement were used: complete consistency, when the physicians agreed with the CDSS recommendations; partial consistency, when the physicians didn’t agree with the CDSS recommendations, but the difference was in the range of ±15%; complete inconsistency — the difference more than ±15%; acceptable consistency is the sum of full and partial consistency (± 15% error is clinically acceptable). The null hypothesis of the study was the absence of difference in consistency/inconsistency between physicians and the CDSS.
RESULTS: The frequency of full consistency between CDSS and physician recommendations for initiating insulin pump therapy is 29.8-43.8%, and inconsistency is 33.7-41.1%. Acceptable consistency is 58.9–66.3%. There were no significant differences in mean insulin pump parameters between CDSS and physicians.
CONCLUSION: The results obtained are consistent with previous studies. Proposed model demonstrates acceptable performance regarding initial CSII settings, without significant deviations between various parameters.
BACKGROUND: The level of glycemia at different points of the glucose tolerance test measure different phases of insulin secretion, accordingly the groups of pregnant women with GDM diagnosed at different points of the test have differences.
AIM: to evaluate the impact of oral glucose tolerance test results for frequency of insulin treatment, incidence of preeclampsia and pregnancy outcomes in women with GDM.
MATERIALS AND METHODS: Retrospective analysis of 200 maternal medical cards and hospital cards of birth in women with GDM for the period 2021–2022. The patients were divided into two groups according the results of OGTT: 1st group — 102 pregnant women with fasting hyperglycemia, 2nd group — 98 pregnant women with hyperglycemia in 1 and 2 hours after glucose intake. Differences in age, body weight, BMI, weight gain during pregnancy, therapy of GDM were studied, and the incidence of preeclampsia and pregnancy outcomes were assessed in both groups.
RESULTS: women of the 1st group had significantly higher weight and initial BMI. Pregnant women of both groups with a BMI over 25 kg/m2 more often required insulin treatment. The incidence of preeclampsia, newborn weight and the incidence of macrosomia were higher in 1st group.
CONCLUSION: Fasting hyperglycemia in OGTT is associated with overweight and obesity, and these women are more likely to require insulin therapy. Women with GDM diagnosed by fasting hyperglycemia are at grate risk of developing preeclampsia and macrosomia.
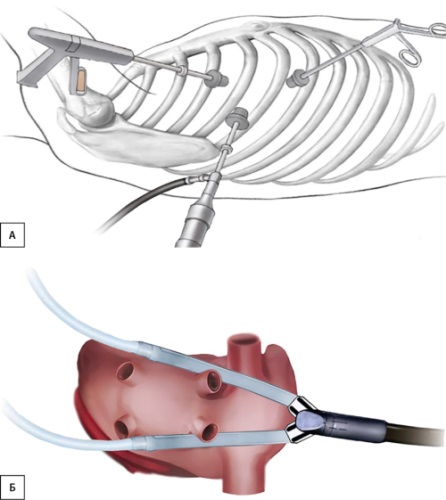
BACKGROUND: Treatment of patients with diabetes mellitus (DM) and a long-term persistent form of atrial fibrillation (AF) is an unsolved problem of the healthcare system due to a high risk of disability and mortality. Considering low effectiveness of drug treatment for AF, surgical technologies have been introduced into clinical practice in most countries, but their effectiveness has not been validated for patients with DM. According to various researches isolated interventional treatment of patients with AF and DM is associated with a high rate of recurrence compared to patients without disorders of carbohydrate metabolism. The feasibility of using other surgical approaches (the isolated thoracoscopic procedure or the isolated thoracoscopic procedure in combination with intracardiac intervention) for the treatment of AF for patients with DM has not been determined yet.
AIM: To evaluate the effectiveness and safety of a staged surgical approach to release patients with DM from AF.
MATERIALS AND METHODS: The study included 19 patients aged 53–73 with DM and long persistent AF. Among them there were 4 (21,4%) women and 15 (78,9%) men. To maintain sinus rhythm all patients were undergone with thoracoscopic epicardial ablation. In three mounts, later the invasive electrophysiological studies and radiofrequency ablation were carried out due to reconnection of left atrium (LA).
RESULTS: At the end of the blinded period sinus rhythm was maintained for 17 (89,5%) patients during the observation period. Two patients (10.5%) had AF recurrence. In both cases, the second stage of treatment wasperformed (electrophysiology study and endocardial ablation). Amid normal sinus rhythm after thoracoscopic epicardial ablation the volume of the LA (p=0,013) and the N-terminal prohormone of brain natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) (p=0,014) significant decreased. No adverse events were recorded in the perioperative or long-term periods.
CONCLUSION: Аccording to our pilot study, the staged approach to surgical maintenance of sinus rhythm for patients with diabetes and persistent form of atrial fibrillation can be an optimal strategy. The endocardial stage could be performed for this category of patients in case of recurrence of tachysystolic cardiac arrhythmias.
BACKGROUND: Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is a disease with high prevalence and early mortality, and identifying groups at risk for adverse outcomes is important in secondary prevention.
AIM: To study clinical, metabolic and genetic risk factors for deaths in various clinical phenotypes in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus in the Novosibirsk region.
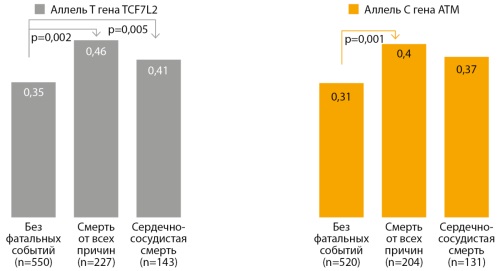
MATERIALS AND METHODS: A prospective cohort study was conducted of 2507 patients with T2DM. The follow-up duration was 6.3±2.5 years. Depending on the level of C-peptide and the HOMA-IR index, patients were divided into 3 phenotypes: insulinopenic (n=288), classic (n=1921), insulin-resistant (n=298). Fatal outcome for the period from 2014 to 31.12.2022 was recorded in 592 patients (23.6%). DNA isolation and genotyping of structural variants of the TCF7L2(rs7903146), ATM(rs11212617) genes were performed by PCR.
RESULTS: The main cause of death in patients with T2DM in all phenotypes was CVD (63.8%). Patients with an insulin-resistant phenotype had a significantly shorter duration of diabetes at the time of death, 12.3±5.5 years, compared with the classic and insulinopenic phenotype (p<0.001). Risk factors for mortality from all causes according to multivariate Cox regression analysis (OR) were the duration of T2DM (1.043, p<0.001), the level of HbA1c (1.131, p<0.001), creatinine (1.013, p=0.002), the T allele of the TCF7L2(rs7903146) gene (OR=1.431, p=0.017) and allele C of the ATM(rs11212517) gene (OR=1.509, p=0.007). Predictors of cardiovascular death were HbA1c (OR=1.129, p=0.001), duration of diabetes (OR=1.041, p=0.002), creatinine level (OR=1.015, p=0.004), the T allele of the TCF7L2(rs7903146) gene (OR=1.719, p=0.005) and allele C of the ATM gene (OR=1.539, p=0.024).
CONCLUSION: The study found that patients with an insulin-resistant had a poor prognosis. The main predictor of general and cardiovascular death was HbA1c. The T allele of the TCF7L2(rs7903146) gene increased the risk of overall mortality by 43.1%, the C allele of the ATM(rs11212617) gene by 50.9%.
Review
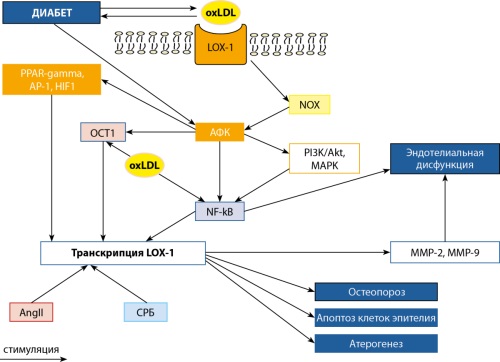
INTRODUCTION. Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) occurs in 8.5% of the adult population with a tendency to increase. A characteristic feature of T2DM is dyslipidemia. One of its manifestations includes accumulation of increased concentration of oxidized low-density lipoproteins (ox-LDL) in circulation. Ox-LDL molecules act on cells through LOX-1 receptors.
THE PURPOSE OF THE REVIEW is to demonstrate results of studies presented in publications of 2010–2024 (PubMed, RSCI) indicating the pathogenetic role of ox-LDL and its LOX-1 receptors in T2DM development and course.
MATERIALS AND METHODS. In the analysis of more than 2800 literature sources (PubMed), in which together with term “diabetes mellitus” keywords are found: ox-LDL (1150 sources) or LOX-1 (159 sources), as well as OLR1 (106 sources), 50 sources were identified that are directly related to T2DM and the studied functionally related markers — the LOX-1 receptor and its ligand ox-LDL.
RESULTS. LOX-1 is scavenger receptor that uses ox-LDL as its proper ligand. Gene OLR1 encodes ox-LDL receptor, LOX-1. The linking of T2DM and circulating levels of ox-LDL is bidirectional. The emerging insulin resistance directly correlates with oxidation of low-density lipoproteins, which is observed in more than 80% of patients and depends on the duration of T2DM. High plasma ligand levels are associated with increased type 2 diabetes risk. The mechanism of this association is thought to be related to functionally significant expression of LOX-1 on pancreatic cells. It was shown that pancreatic β-cells in the presence of ox-LDL increased production of the inducible early repressor of the cAMP signaling pathway, ICER. As result of ICER action, insulin production and secretion ceased. Increased ox-LDL concentrations are a pathogenetically significant factor in the development of atherosclerotic vascular lesions, as they stimulate the generation of foam cells. Ox-LDL-LOX-1-mediated interactions on the vascular surface led to endothelial dysfunction with subsequent development of tissue hypoperfusion and organ dysfunction.
CONCLUSION. Circulating ox-LDL, in interaction with its receptor LOX-1, makes a significant contribution to the development of T2DM, promoting its progression. Increased concentration of ox-LDL in blood increases the risk of severe T2DM, leading to endothelial dysfunction and promoting the development of atherosclerotic vascular lesions.
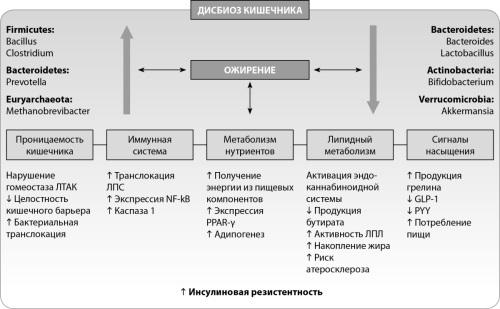
Obesity, type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), and related metabolic disorders occupy the leading positions on the lists of diseases worldwide. It is not surprising that the efforts of many scientific groups and clinicians are aimed at finding effective therapeutic strategies to treat these diseases. In recent decades, the involvement of the intestinal microbiota in the pathogenesis of metabolic, immune, and other disorders in humans has become increasingly obvious. In this regard, attempts are made to modulate the composition and functional activity of the microbiota as a primary or adjuvant way of treating various disorders. The purpose of this review was to highlight and analyse the results of clinical studies in recent years devoted to the study of various methods of modulating the intestinal microbial community for the treatment of obesity, metabolic syndrome, and T2DM. To achieve this goal, we conducted a systematic search using electronic databases, including Scopus, Medline, and PubMed, limiting the publication period from 2019 to 2024. The conducted analysis showed that the therapeutic success of various methods of modulating intestinal microbiota, on the one hand, indicates the need to take into account the characteristics of the microbial composition of the intestines of patients and direct therapeutic actions to correct dysbiosis; on the other hand, it provides grounds for the widespread introduction of pharmacological or other approaches to correcting the microbiotic composition of the intestine as an effective method of treating obesity and associated metabolic disorders.
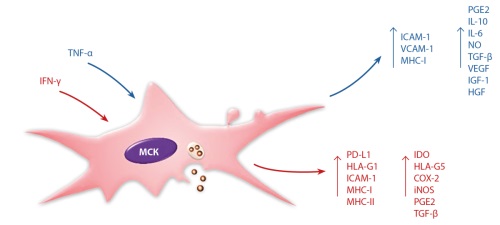
In patients with diabetes mellitus (DM), systemic disorders in the body can cause a number of complications. One of the main complications is the disruption of wound healing processes, which can lead to the development of a diabetic foot ulcer (DFU) and subsequent amputation of the limb. Modified mesenchymal stem cells (GM-MSCs) - as a means of treating chronic wounds, reduce homing, have increased proliferative potential, therapeutic antitumor and pancreas-supporting properties. Native and genetically modified cells from allogeneic or autologous sources are studied for the treatment of DFU. The review presents the world experience of using stem cells in therapy in preclinical and clinical studies, collects data on the proposed technologies for the treatment of diabetic ulcers using GM-MSCs: combined transplantation of GM-MSCs with pancreatic islets, regulation of migration processes by changing the expression of integrins, blocking estrogen signals, increased expression of a number of genes, such as SDF-1α, c-JUN, MALAT1, to increase the viability and stimulate the proliferation of mesenchymal stem cells. Cells temporarily carrying therapeutic genetically engineered constructs show high efficiency of their use in preclinical trials.
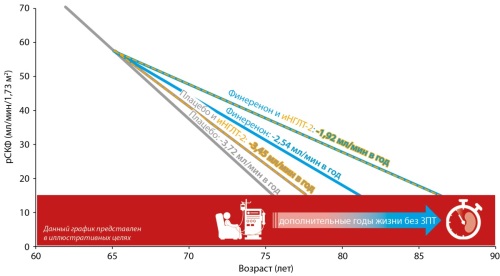
The main factor in modern healthcare is to increase the length and quality of life of patients, especially with socially significant diseases, such as type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) and its dangerous complication — chronic kidney disease (CKD), associated with a high rate of cardiovascular diseases (CVD), end-stage renal disease and mortality. Effective management of cardiorenal risks in addition with blockers of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system and sodium-glucose cotransporter type 2 inhibitors was replenished in 2023 with a new non-steroidal selective mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist — Finerenone. This unique and one-of-a-kind drug improves the control of cellular processes, fibrosis in the kidneys and myocardial remodeling. This review presents the main studies on the mechanism of action of Finerenone, assessment of its effectiveness and safety, and its effect on the risk of developing cardiorenal risk in patients with T2DM. Finerenone is one-of-a-kind drug who has no alternatives to improve a control of cellular processes, a fibrosis in the kidneys and a myocardial remodeling. In this review we presented Finerenone effects on an eGFR slope as a main kidney function feature, and proposed practice points on safe initiation of the three cardiorenal «pillars» in patients with T2DM in accordance with the current clinical guidelines.
Editorial note
Erratum
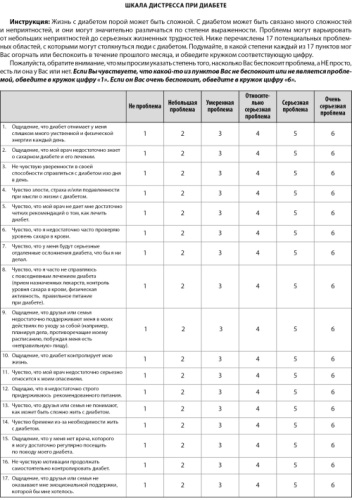
A corrigendum on «Adaptation of The Diabetes Distress Scale on a Russian-speaking sample of patients with type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus» authored by Natalia V. Likhodey, Vitalii E. Epishin, Marina F. Kalashnikova, Aleksandra M. Kaurova, Margarita V. Tulupova, Yulia P. Sych, Irina B. Bondareva (2024). Diabetes Mellitus. 27(5). https://doi.org/10.14341/DM13150.
An error was made in the article. In the final version of the article, the order of questions in Figure 1 and Table 4 does not correspond to the version of the questionnaire used during data collection. This discrepancy occurred because two English versions of the questionnaire, differing in the order of questions 1 and 2, were initially used in the study.
The correct order of questions in The Diabetes Distress Scale is as follows:
Question 1: Feeling that diabetes taking up too much of my mental and physical energy every day.
Question 2: Feeling that my doctor doesn’t know enough about diabetes and diabetes care
The editorial board regrets this error. The original version of the article has been replaced.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0).
ISSN 2072-0378 (Online)