Перейти к:
Влияние циркадных ритмов на углеводный обмен в норме и при сахарном диабете
https://doi.org/10.14341/DM13241
Аннотация
Большинство процессов в организме человека и других живых организмов подчинено биоритмам. Под термином «Биоритмы» понимают периодически повторяющиеся изменения биологических процессов. Биологические ритмы наследственно закреплены и являются важнейшими факторами естественного отбора и адаптации организмов. Циркадные ритмы у человека регулируются центральными и периферическими часами. Центральные часы расположены в супрахиазматическом ядре (СЯГ) переднего гипоталамуса, а периферические часы находятся в различных тканях и органах организма человека, включая мозг, поджелудочную железу, печень, жировую ткань, желудочно-кишечный тракт и мышцы. Внешние и внутренние сигналы находятся в постоянной синхронизации и обеспечивают гомеостаз. Несоответствие внутренних биологических часов с внешними сигналами может приводить к десинхронизации циркадных ритмов. Десинхронизация циркадного ритма может приводить к возникновению метаболически-ассоциированных заболеваний, в том числе к развитию сахарного диабета 2 типа (СД2), ожирению и к худшему контролю гликемии. В этой статье рассматриваются влияние циркадных ритмов на биологические процессы и на секрецию гормонов, также связь между циркадными ритмами и метаболизмом глюкозы у людей с СД2 и нормогликемией.
Для цитирования:
Мисникова И.В., Золоева Д.Э. Влияние циркадных ритмов на углеводный обмен в норме и при сахарном диабете. Сахарный диабет. 2025;28(4):367-375. https://doi.org/10.14341/DM13241
For citation:
Misnikova I.V., Zoloeva D.E. The influence of circadian rhythms on carbohydrate metabolism in health and in diabetes mellitus. Diabetes mellitus. 2025;28(4):367-375. (In Russ.) https://doi.org/10.14341/DM13241
ВВЕДЕНИЕ
Сахарный диабет 2 типа (СД2) является серьезной социальной медицинской проблемой вследствие высокой распространенности и повышенного риска развития кардио-ренальной патологии. Ожирение и метаболический синдром значительно увеличивают риск развития СД2 [1]. Изучение факторов, лежащих в основе развития ожирения, метаболического синдрома и СД2, является важнейшей задачей современной науки, так как выяснение их роли может раскрыть новые возможности в профилактике и лечении СД2. В последнее время значительный интерес вызывает участие циркадной системы в развитии метаболических нарушений, которая является основным регулятором большинства физиологических процессов в организме человека. В настоящее время появляется все больше доказательств, связывающих нарушения циркадного ритма не только с ключевыми компонентами метаболического синдрома, но и с его основными сопутствующими заболеваниями, включая нарушения сна, депрессию, стеатогепатит и когнитивную дисфункцию. Исходя из этого, в 2019 г. группа ученых (Zimmet P., Alberti K.G.M.M., Stern N., Bilu C., El-Osta A., Einat H., Kronfeld-Schor N.) предложила переименовать метаболический синдром в «циркадный синдром», обосновывая это важностью нарушений циркадного ритма в качестве этиологического фактора, лежащего в основе метаболического синдрома [2]. Исследование на китайской популяции показало, что циркадный синдром является лучшим предиктором сердечно-сосудистых заболеваний, чем метаболический [3].
ФИЗИОЛОГИЯ ЦИРКАДНЫХ РИТМОВ
Практически все физиологические процессы в организме подчинены циркадным ритмам, около 24-часовым биологическим колебаниям, которые поддерживают течение физиологических процессов в синхронизации с внешней средой — геофизическим временем [4]. Не являются исключением процессы, обеспечивающие определенный уровень глюкозы крови: глюконеогенез в печени и почках [5].
Организм человека использует экзогенные сигналы — так называемые зейтгеберы, в переводе с немецкого — «дающие время», благодаря которым различные физиологические процессы соотносятся с циркадными ритмами. Степень освещенности является основным, но не единственным зейтгебером. Также к экзогенным стимулам, регулирующим циркадные ритмы, относятся прием пищи, температура окружающей среды, физические упражнения, социальное взаимодействие, медикаментозные препараты и обучение [6][7]. В нормальных физиологических условиях все зейтгеберы тесно взаимосвязаны. Но существует и эндогенная регуляция — внутренние биологические часы, хорошо скоординированная система обратной связи, поддерживающая циркадную регуляцию. Она включает в себя контроль над экспрессией мРНК, стабильностью белка, состоянием хроматина, а также синтеза и действия метаболитов для соблюдения циркадных ритмов. К центральным биологическим (циркадным) часам относится СЯГ. Это координационный «часовой» центр, который служит для обработки информации от сигналов внешней и внутренней среды, и для оповещения о времени суток для периферических клеток [8]. Свет попадает на сетчатку глаза, где во внутренних слоях находятся светочувствительные ганглиозные клетки сетчатки. Они генерирует сигнал об уровне освещенности, который поступает на вентромедиальную группу нейронов в СЯГ, которое синхронизирует свои собственные нейронные клеточные часы. В СЯГ возникает циркадная ритмичность — эндогенное колебание активности различных функций с почти 24-часовым периодом [9]. Циркадные часы контролируют уровень глюкокортикоидов через гипоталамо-гипофизарно-надпочечниковую ось (ГГНО), что обуславливает непосредственное влияние на углеводный обмен [10].
На периферии в каждой клетке имеется свой часовой механизм, сопряженный с главными часами в СЯГ. Эти периферические ритмы имеют уникальную фазовую связь с основными часами, которая координируется через нейронные пути, нейропептиды и гормоны [11]. Биологические часы представляют из себя группы молекул в клетках, распределенных по всему организму [12]. Циркадный ритм передается в другие области мозга и на периферию через прямые нейронные связи с другими частями гипоталамуса, а также через симпатическую нервную систему и ряд гормональных сигналов. Периферические часы интегрируют сигналы СЯГ с факторами окружающей среды, образом жизни и собственными автономными ритмами, тем самым поддерживают циркадный ритм энергетического обмена организма [13]. Центральные часы связаны с периферическими посредством эндокринной системы [14].
ЦИРКАДНЫЙ РИТМ НА МОЛЕКУЛЯРНОМ УРОВНЕ
Циркадная регуляция на молекулярном уровне осуществляется за счет двух петель обратной связи [15], которые находятся под контролем часовых генов. Часовые гены играют определяющую роль в работе как отдельных клеток, так и всего организма. К важным часовым генам относят:
- гены периода (PER1, PER2, PER3);
- гены криптохрома (CRY1, CRY2);
- ген TIM (TIMELESS);
- ген мозгового и мышечного аналога ядерного транслокатора ариловых углеводородов brain and muscle aryl hydrocarbon nuclear translocator (BMAL1 или ARNTL);
- ген циркадных локомоторных выходных циклов circadian locomotor output cycles kaput (CLOCK);
- гены reverse strand of ERBA REV-ERBα и β (член суперсемейства ядерных рецепторов лиганд-регулируемых факторов транскрипции);
- ген ROR — ретиноид-связанные орфанные рецепторы, участвует в метаболических процессах.
Двумя наиболее изученными белками, продуцируемыми часовыми генами, у млекопитающих являются белки CLOCK и BMAL1, которые связываются друг с другом, накапливаются в цитоплазме, потом переходят в ядро клетки и там прикрепляются к специальному участку на дезоксирибонуклеиновой кислоте (ДНК) под названием E-box [16][17]. К началу темного времени суток их концентрация достигает максимума. Белки BMAL1 и CLOCK активируют транскрипцию и трансляцию генов PER 1-3, CRY, что происходит рано утром. К полудню образуется максимальное количество белков PER и CRY. К вечеру белки PER и CRY транслоцируются в ядро и взаимодействуют с BMAL1 и CLOCK, тем самым подавляя их активность. Потом PER и CRY постепенно распадаются, высвобождаются молекулы BMAL1 и CLOCK, чтобы начать новый суточный цикл. Это образует первую петлю обратной связи.
Во второй петле обратной связи гены REV-ERBα и REV-ERBβ, ROR подавляют BMAL1 (рис. 1) [18]. REV-ERBα участвует в метаболизме липидов и глюкозы, термогенезе, дифференцировке адипоцитов и мышц, а также в биогенезе митохондрий. Недавние исследования в области циркадных ритмов и метаболизма обнаружили, что ген REV-ERBα является важным элементом в регуляции циркадных ритмов и метаболизма у животных и у человека. Этот ген отвечает за функции как центральных, так и периферийных часовых систем организма. У людей несколько полиморфизмов REV-ERBα связаны с увеличением риска ожирения и метаболического синдрома. Особенно важная его роль проявляется в тканях поджелудочной железы, где он регулирует секрецию глюкагона и инсулина, регулирует пролиферацию β-клеток поджелудочной железы и гены, участвующие в метаболизме липидов. Таким образом, REV-ERBα играет ключевую роль в нескольких процессах, связанных с физиологией α и β-клеток поджелудочной железы.
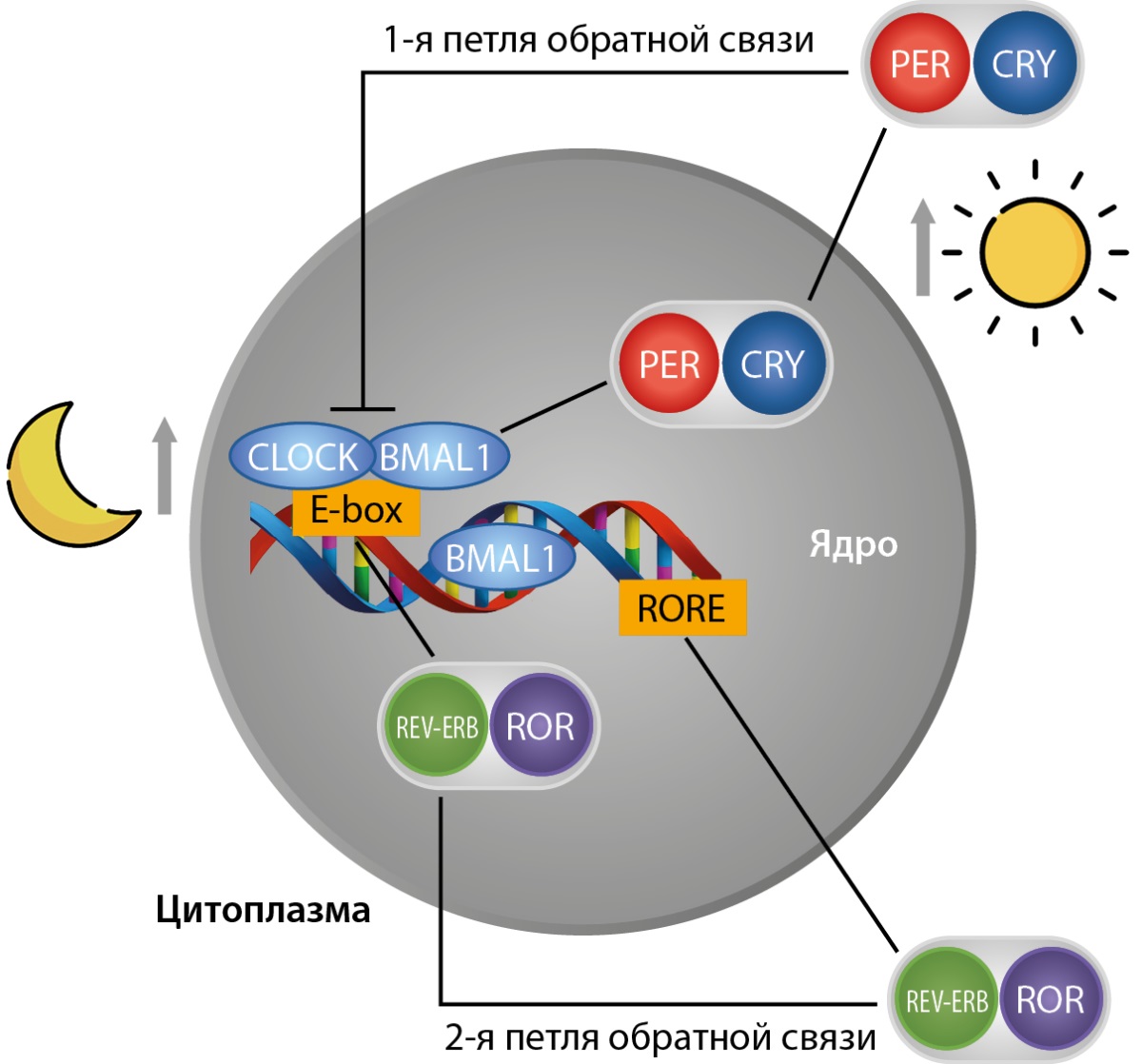
Рисунок 1. Схематическое изображение молекулярной структуры циркадных часов (адаптировано из работы Vieira и соавт., 2015 г.) [18].
Примечание: CLOCK — ген циркадных локомоторных выходных циклов circadian locomotor output cycles kaput; BMAL1 — ген мозгового и мышечного аналога ядерного транслокатора ариловых углеводородов brain and muscle aryl hydrocarbon nuclear translocator; E-box — регуляторный участок ДНК; ROR — ретиноид-связанные орфанные рецепторы, ген, который участвует в метаболических процессах; REV-ERB — член суперсемейства ядерных рецепторов лиганд-регулируемых факторов транскрипции; PER — ген периода; CRY — ген криптохрома.
1 петля обратной связи показывает, что белки — активаторы CLOCK и BMAL1 прикрепляются к участку E-box и активируют транскрипцию и трансляцию генов PER и CRY, что происходит рано утром. К вечеру эти гены транслоцируются в ядро и взаимодействуют с BMAL1 и CLOCK, подавляя их активность.
2 петля обратной связи показывает, что CLOCK и BMAL1 связываются с E-box и с генами REV-ERB и ROR. ROR способствует активации транскрипции гена BMAL1 и подавлению REV-ERB. REV-ERB и ROR подавляют BMAL1.
ЗАВИСИМОСТЬ МЕТАБОЛИЗМА ГЛЮКОЗЫ ОТ ЦИРКАДНОЙ РЕГУЛЯЦИИ
Циркадные часы влияют на метаболизм глюкозы, холестерина, секрецию инсулина, глюкагона и лептина. Центры в супрахиазматических ядрах гипоталамуса осуществляют циркадную регуляцию через нейроэндокринную и вегетативную систему [19], поэтому секреция многих гормонов и нейромедиаторов подчинена суточным колебаниям (рис. 2).
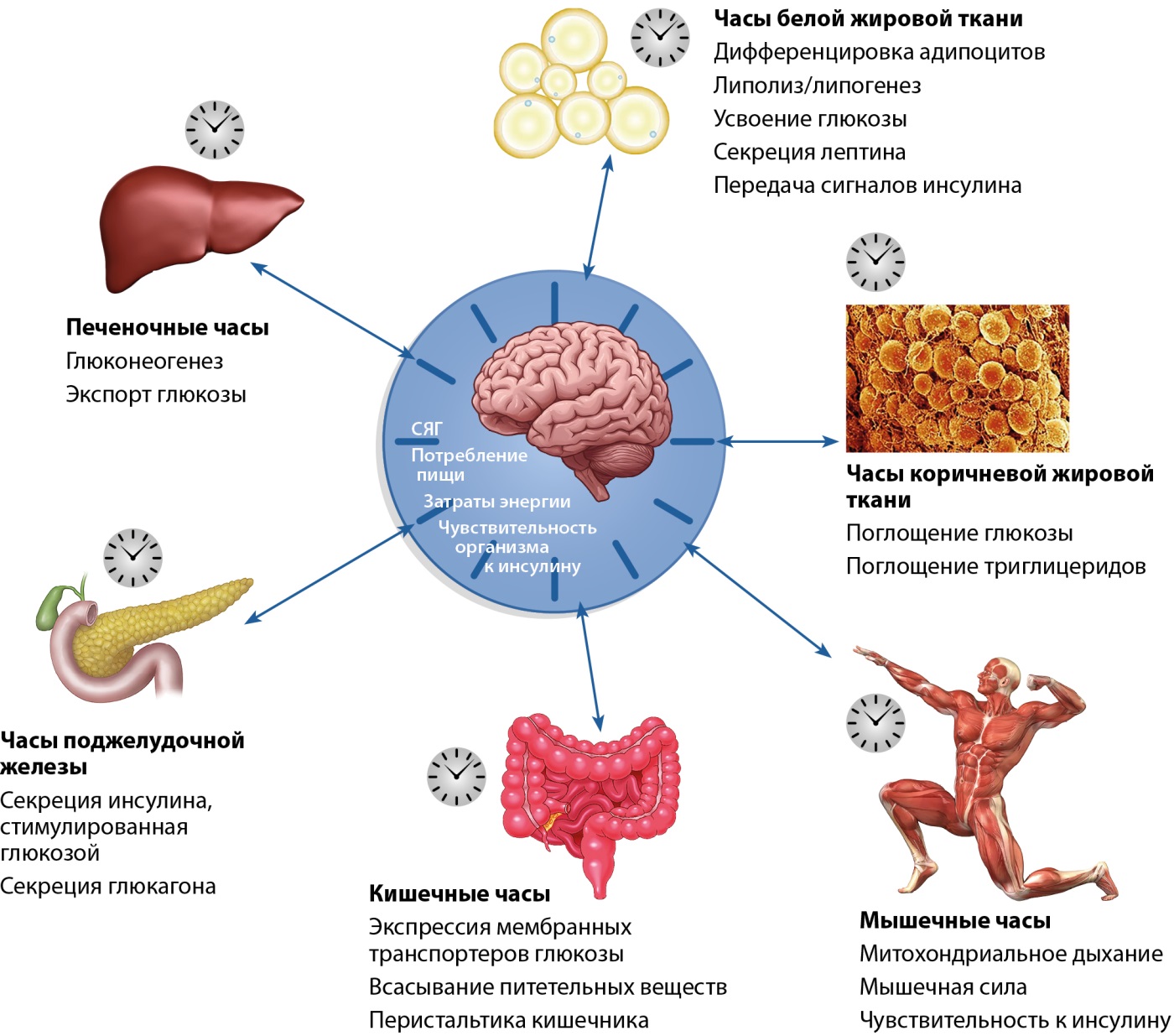
Рисунок 2. Метаболические процессы, подверженные циркадной регуляции (адаптировано из работы Stenvers и соавт., 2019 г.) [20].
СЯГ — супрахиазмальное ядро гипоталамуса
ЦИРКАДНЫЕ КОЛЕБАНИЯ ГЛЮКОЗЫ У ЛИЦ С НОРМОГЛИКЕМИЕЙ
Толерантность к глюкозе изменяется в течение суток, причем у лиц без нарушений углеводного обмена утром толерантность к глюкозе выше, чем вечером [20]. При нормогликемии постпрандиальный пик после одинакового по составу приема пищи выше в ужин, чем в завтрак, поскольку чувствительность к инсулину достигает максимума в утренние часы [21]. Это отличие не зависит от времени сна и бодрствования [22]. Концентрации инсулина, С-пептида и глюкагона меняются в зависимости от времени суток. Так, инсулин в постпрандиальном периоде ниже в ужин, С-пептид выше после обеда, а глюкагон выше после завтрака [23]. Во многом суточный ритм толерантности к глюкозе определяется изменениями в чувствительности тканей к инсулину и в чувствительности к глюкозе β-клеток поджелудочной железы (то есть глюкозоиндуцированной секреции инсулина поджелудочной железой).
Инсулин и циркадные ритмы влияют друг на друга. Между циркадными часами и циркадными вариациями секреции инсулина существует двунаправленная связь. Благодаря циркадной регуляции секреция инсулина β-клетками поджелудочной железы достигает максимума с полудня до 18:00 и снижается между полуночью и 06:00 [24]. Инсулинорезистентность также регулируется циркадными часами. У лиц без сахарного диабета чувствительность к инсулину максимальна в утренние часы и минимальна вечером [20]. Циркадные часы определяют изменения в секреции кортизола, мелатонина и гормона роста, каждый из этих гормонов может оказывать влияние на чувствительность к инсулину. Следовательно, усиление или ослабление их секреции может изменять и степень инсулинорезистентности.
Кортизол влияет на показатели гликемии, липолиз, гликолиз, активность автономной нервной и иммунной систем, сердечно-сосудистую систему, головной мозг, настроение, сон и бодрствование [25]. Кортизол воздействует на сигнальные пути инсулина, ухудшает чувствительность к инсулину в ряде тканей, снижая поглощение глюкозы и способствуя развитию инсулинорезистентности [26]. Синтез кортизола имеет 24-часовой циркадный ритм. Максимальная концентрация кортизола приходится на ранние утренние часы на 07:00–08:00, более низкие значения кортизола отмечаются в 02:00–04:00. Суточные колебания уровня кортизола стабильны, но изменения окружающей среды могут повлиять на уровень кортизола, например, острый или хронический стресс способствуют повышению его уровня. В свою очередь кортизол выполняет важную роль в регуляции циркадного ритма, он участвует в передаче циркадного сигнала из СЯГ в периферические ткани. Так, концентрация кортизола способна изменять биологические ритмы жировой ткани человека [27]. Нарушения циркадной регуляции кортизола могут повлиять на центральные и периферические часы. Кортизол воздействует на экспрессию часовых генов через рецепторы глюкокортикоидов в цитоплазме клеток-мишеней, активирует неактивное комплексное состояние цитоплазматического рецептора и подвергает его структурным изменениям. Глюкокортикоидный ответ регулирует экспрессию нескольких генов, в том числе PER1, PER2, NPAS2 и REV-ERBβ [28].
Прием пищи ассоциирован с изменением в уровне кортизола [29]. Ограничение приема пищи, который включает в себя пропуск ужина, может обеспечить лучшее чувство бодрости утром, так как более низкий уровень кортизола ночью может улучшить качество сна, а более высокий утренний кортизол повышает бодрствование [30].
Мелатонин является еще одним гормоном, секреция которого тесно связана с циркадными ритмами. Усиление секреции мелатонина в темное время суток приводит к снижению чувствительности к инсулину. Мелатонин передает сигнал из СЯГ в периферические часы. Основным зейтгебером в секреции мелатонина является свет-темнота. На синтез мелатонина влияет как дневной естественный свет, так и искусственное освещение в ночное время. Концентрация мелатонина изменяется от воздействия света, сменной работы, проживания в близости полюсов Земли. Главной функцией этого гормона в организме является стимулирование сна, модуляция гормонов гипофиза и надпочечников, регуляция уровня глюкозы также участвует в иммунном ответе. Мелатонин влияет на качество сна, колебания его концентраций влияют на состояние бодрствования. Высокая световая волна подавляет мелатонин в крови. Длительное регулярное воздействие света может смещать циркадный ритм мелатонина [31]. Мелатонин имеет рецепторы в СЯГ и в β-клетках поджелудочной железы, способен блокировать секрецию инсулина, которая стимулируется глюкозой [32]. Отсутствие мелатонина у крыс приводило развитию устойчивой резистентности к лептину и развитию избыточной массы тела, а лечение мелатонином снизило потребление пищи, массу тела и ожирение [33].
Гормон роста, секреция которого также подвержена циркадной регуляции через контроль цикла «сон-бодрствование», является контринсулярным гормоном и препятствует действию инсулина в печени и мышцах. Нарушения циркадных механизмов, в частности в ритме BMAL1, могут провоцировать изменения в секреции гормона роста и половых гормонов, что способствует инсулинорезистентности. Депривация сна, поздний хронотип, социальный джетлаг и сменная работа связаны с прогрессированием инсулинорезистентности. Полиморфизмы гена CLOCK также тесно связаны с инсулинорезистентностью. Циркадный ритм концентрации циркулирующего инсулина, в свою очередь, играет важную роль в синхронизирующем действии некоторых часовых генов, в частности PER1 и PER2. Гормон роста секретируется соматотрофами гипофиза. Максимальная концентрация приходится на ночное время и минимальная — перед пробуждением. Суточный ритм гормона роста регулируется СЯГ и соматотрофами. Гормон роста увеличивает липолиз и влияет на толерантность к глюкозе. Повышение гормона роста во время раннего сна может повышать толерантность к глюкозе в середине сна у лиц с нормогликемией, в то время как повышение его до пробуждения может ухудшать толерантность к глюкозе [34].
Синтез глюкагона также подвержен циркадным колебаниям: секреция инсулина в ночное время суток снижается, а глюкагона — увеличивается, чтобы стимулировать глюкозу в печени и поддерживать ее уровень. Ежедневные колебания в плазме гормонов поджелудочной железы также могут поддерживаться независимо от поведения при голодании или приеме пищи.
Лептин — еще один важный маркер циркадного ритма. Лептин вырабатывается в адипоцитах и имеет рецепторы в гипоталамусе, пик концентрации достигается в ночное время. Этот гормон регулирует метаболизм, увеличивает термогенез за счет активации тиреоидных гормонов и активизирует симпатическую нервную систему, что приводит к усилению потребления энергии. Лептин ингибирует синтез аденозинтрифосфата (АТФ) в митохондриях, что способствует потреблению энергии в виде тепла. Нарушение циркадного ритма может повлиять на секрецию лептина, термогенез и энергетический гомеостаз [35][36].
ФАКТОРЫ, ВЛИЯЮЩИЕ НА ЦИРКАДНУЮ РЕГУЛЯЦИЮ УГЛЕВОДНОГО ОБМЕНА
Время приема пищи (поздний завтрак и поздний ужин)
Изменения времени приема пищи могут нарушить хорошо построенную координацию и, как следствие, также изменить циркадную ритмичность многих гормонов, участвующих в метаболизме, таких как инсулин, глюкагон, адипонектин, кортикостерон, лептин, липокаин и висфатин [37]. По данным исследований, поздний первый прием пищи ассоциирован с развитием СД2 [38], а пропуск ужина связан с более низкими рисками прибавки массы тела и развитием ожирения [23]. Пропуск завтрака и поздний первый прием пищи могут способствовать увеличению уровня глюкозы в течение 24 часов и нарушать реакцию инсулина на глюкозу, что, в свою очередь, увеличивает риск развития СД2 [39].
Прием пищи незадолго до сна может приводить к дополнительному подъему гликемии по сравнению с более ранним приемом пищи. Мелатонин блокирует секрецию инсулина, которая стимулируется глюкозой после приема пищи [40]. Это может провоцировать неадекватный инсулиновый ответ после позднего ужина и постпрандиальную гипергликемию.
Ночной прием пищи может приводить к десинхронизации между периферическими и центральными часами, так как постоянные изменения во времени приема пищи могут нарушить циркадные ритмы, что в свою очередь может привести к неблагоприятным последствиям для здоровья [41].
Западная диета
Рацион является еще одним важным фактором, который влияет на циркадные ритмы. Исследования показали, что диета с высоким содержанием жиров у мышей влияет на их активность, меняя время, когда они наиболее активны. Это также связано с изменениями в работе генов, которые отвечают за циркадные ритмы, а также с ядерными рецепторами, которые регулируют факторы, управляющие этими ритмами. Эти изменения затрагивают гены, участвующие в использовании энергии в гипоталамусе, печени и жировых клетках [42][29]. Анализ 10 486 взрослых (когорта NHANЕS), средний возраст которых составил 50 лет, показал практически двукратное возрастание риска циркадного синдрома у приверженных западной диете, и снижение риска его развития на так называемой «разумной» диете [43]. Западный тип питания характеризовался высоким потреблением рафинированных зерен, твердых жиров, сыра, сахаров, копченого мяса, красного мяса, томатов и томатных продуктов, яиц и заменителей яиц, а также белого картофеля. В то же время люди, придерживающиеся «разумной» диеты, потребляли много овощей (красных, оранжевых, темно-зеленых и других), масла, орехи и семена, цельного зерна, фруктов, йогурта, морепродуктов и соевых продуктов. Циркадные нарушения у приверженцев западной диеты могут быть спровоцированы употреблением большого количества жиров. Протекторный эффект «разумной» диеты на циркадную регуляцию можно частично объяснить наличием в продуктах питания мелатонина и его предшественника триптофана, поскольку мелатонин является регулятором циркадных ритмов [44].
Поздний хронотип
Время пика физической и умственной активности в течение дня несколько отличается. И на основании этих отличий определяется хронотип человека. Также разделение на хронотипы проводят на основании временной точки — середины ночного сна (СНС):
- поздний (СНС≥04:00);
- средний (СНС от 02:30 до 04:00);
- ранний (СНС<02:30).
Люди с поздним хронотипом имеют повышенный риск развития СД2, а также больший вес и окружность талии. J.H.P. van der Velde и его коллеги из Медицинского центра Лейденского университета (Нидерланды) определили хронотип у 5026 человек и оценили риск развития СД2. В течение периода наблюдения в 6,5 года у лиц с поздним хронотипом на 46% чаще развивался СД2, был больший процент висцерального жира и на 14% больше жира в печени [45].
Повышение риска СД2 у лиц с поздним хронотипом может быть вызвано несколькими причинами. Ранний хронотип ассоциируется с более выраженным пиком в секреции кортизола в утренние часы, который менее выражен у лиц с поздним хронотипом [46]. Изменения в ритмах секреции кортизола ведут к нарушениям метаболизма глюкозы, увеличению продукции глюкозы печенью, развитию инсулинорезистентности и могут приводить к СД2 [28].
В силу ряда причин у лиц с утренним и промежуточным хронотипом время приема пищи также может сдвигаться на более поздние часы, что может быть ассоциировано с худшими показателями метаболизма по сравнению с более ранним приемом пищи, соответствующим данным хронотипам [47].
Ночные смены
Образ жизни играет важную роль в поддержании биологических ритмов. Сменная работа способна нарушать биоритм, так как бодрствование в ночные часы смещает пики в уровне мелатонина, кортизола, изменяется работа периферических циркадных генов. Нарушения этих ритмов могут иметь негативные последствия для метаболического здоровья [48]. В исследованиях у людей со сменной работой наблюдали повышенный уровень артериального давления, триглицеридов и глюкозы, низкий уровень холестерина липопротеинов высокой плотности (ЛПВП) и висцеральное ожирение [49]. Соответственно, у людей со сменной работой имеются повышенные риски развития СД2 и метаболического синдрома [50]. Эти изменения обусловлены тем, что поздний отход ко сну или сокращение времени сна приводят к повышению уровня грелина, снижению уровня лептина, развитию инсулинорезистентности и к увеличению индекса массы тела [14]. Также есть данные, что длительная сменная работа может приводить к различным изменениям в метилировании ДНК и ускорению старения. Существует ассоциация между длительной сменной работой и изменениями в метилировании ДНК гена ZFHX3, который кодирует белок, участвующий в циркадных ритмах [51]. Описано исследование, где выявили, что острая потеря сна у здоровых людей приводит к изменениям метилирования ДНК в жировой ткани по всему геному [52].
Мутации часовых генов
Результаты исследования показывают значительную связь между развитием СД2 и нарушениями в «часовых» генах. [53]. Так, на экспериментальных моделях было показано, что мутации в часовых генах приводили к развитию СД2: мыши с дефицитом или мутацией в генах BMAL1, CLOCK, PER2, CRY имели измененный метаболизм глюкозы и инсулина, что приводит к развитию инсулинорезистентности и ожирению [10].
ВОЗМОЖНОСТИ КОРРЕКЦИИ ЦИРКАДНЫХ НАРУШЕНИЙ
Немедикаментозные методы
В рамках ограничения калорийности важно учитывать циркадные ритмы, поскольку пропуск завтрака и употребление позднего ужина могут негативно сказаться на метаболическом здоровье даже при условии сокращения суточной калорийности. Прием завтрака способствует снижению общего потребления пищи в течение дня, улучшает постпрандиальную гипергликемию (ППГ), чувствительность к инсулину и секрецию глюкагоноподобного пептида-1 (ГПП-1) в последующие приемы пищи. Рекомендации по ограничению калорийности должны учитывать не только суточный расход энергии, но и биологические часы приема пищи, а именно употребление раннего завтрака и раннего ужина [54]. Так как толерантность к инсулину подвержена циркадным ритмам, лицам с нормогликемией необходимо рекомендовать не перегружать ужин углеводами в связи с инсулинорезистентностью в вечернее время. Это позволит улучшить показатели постпрандиального ответа глюкозы и лучше скорректировать массу тела [21].
Изменения в циркадной регуляции глюкозы у пациентов с СД2 должны быть учтены при составлении суточного рациона. Лицам с СД2 необходимо рекомендовать увеличивать количество потребляемой клетчатки и белка на завтрак, расширение физической активности после завтрака, подбирать сахароснижающую терапию с учетом больших подъемов ППГ в утреннее время. При этом рекомендуется употребление более калорийной пищи в первой половине дня, что улучшает постпрандиальные реакции глюкозы и показывает лучшее снижение веса у пациентов с СД2, что играет важную роль в предотвращении развития осложнений СД2 [55].
Продукты, содержащие мелатонин и триптофан, могут положительно влиять на цикл «сон-бодрствование». Мелатонин содержится как в продуктах животного, так и в продуктах растительного происхождения. Такие продукты, как яйца, рыба, мясо, молоко, являются источниками мелатонина, причем концентрация мелатонина выше в яйцах и рыбе, чем в мясе. Из растительных продуктов наиболее богаты мелатонином зерновые, такие как кукуруза, бурый и черный рис, пшеница, овес, ячмень, бобовые, орехи (максимальная концентрация в фисташках), фрукты (виноград, вишня, клубника), овощи (помидор, перец), зерновой кофе [56]. Употребление продуктов, обогащенных триптофаном (например, злаков или белковых продуктов, молока), улучшает показатели сна. Однако механизмы, лежащие в основе этих улучшений, требуют дальнейшего изучения [57].
Медикаментозные методы
Циркадная регуляция может явиться новой терапевтической мишенью при СД2. Так, в качестве нового препарата для лечения СД2 предлагается использовать стабилизаторы криптохрома. TW68 подавляет экспрессию генов Pepck1 и глюкозо-6-фосфатазы, играющих важную роль в глюкогенезе, путем стабилизации CRY1/2, что приводит к снижению уровня глюкозы в крови у мышей, питающихся высокожировой диетой [58].
Интересно, что метформин оказывает влияние на циркадную регуляцию метаболических процессов в печени и мышцах. Прием метформина в вечернее время более эффективен в контроле уровня глюкозы, чем утренний прием. Метформин через активацию аденозин-монофосфат-активированной протеинкиназы (АМПК) приводит к ускорению фазы экспрессии часовых генов и/или метаболических белков в печени и задержке фазы экспрессии в мышцах [59]. Метформин за счет влияния на АМПК может увеличить экспрессию REV-ERBα, который недавно был идентифицирован как внутриклеточный регулятор секреции глюкагона в альфа-клетках [60]. Alex и соавт. исследовали на животных моделях влияние метформина на диабетическую ретинопатию (ДР). Терапия метформином восстанавливала экспрессию часовых генов и Kir4.1 в сетчатке, которые были снижены при ДР [61].
Агонисты PPARγ занимают важную роль в регуляции циркадных часов. Они повышают чувствительность к инсулину и используются для лечения СД2, демонстрируют циркадную экспрессию в печени, жировой ткани и кровеносных сосудах мышей. PPARγ является незаменимым регулятором адипогенеза и может использоваться для лечения метаболических заболеваний. Yang и др. отметили, что пиоглитазон (ПГ) и PPARγ улучшили физиологические параметры и снижали экспрессию генов циркадных часов в печени у мышей с инсулинорезистентностью без ожирения [62]. У мышей прием пиоглитазона в 19:00 был более эффективным, чем в 07:00 у мышей с обратным питанием. Прием ПГ восстановил профиль экспрессии генов часов, снизил уровень NF-κB, p-NF-κB и IL-6, а также увеличил экспрессию Nrf2, Ppar-γ и PPAR-γ. Прием ПГ в 19:00 был более эффективным, чем в 07:00 у мышей с обратным питанием [63].
ЗАКЛЮЧЕНИЕ
Циркадные ритмы являются ключевыми компонентами внутреннего хронометра, обеспечивают слаженную работу биологических систем, позволяя организму адаптироваться к изменениям в окружающей среде. Десинхронизация этих ритмов может приводить к различным метаболическим нарушениям, включая СД2 и ожирение, что подчеркивает важность поддержания баланса между экзогенными и эндогенными факторами. Такие факторы, как время приема и состав пищи, продолжительность сна, отход ко сну, характер работы, лекарственные препараты, важны в поддержании гомеостаза глюкозы и метаболических процессов. Для обеспечения лучшего контроля гликемии и оптимальной массы тела необходимо их учитывать.
Традиционные рекомендации лицам с СД2 сосредоточены на количестве и качестве физической активности, потреблении пищи и приеме лекарств, однако экзогенные циркадные факторы, включая время воздействия света, состав и время приема пищи, лекарственных препаратов, режим сна и бодрствования, также могут оказаться важными для профилактики и лечения инсулинорезистентности, ожирения и СД2.
ДОПОЛНИТЕЛЬНАЯ ИНФОРМАЦИЯ
Источники финансирования. Работа выполнена по инициативе авторов без привлечения финансирования.
Конфликт интересов. Авторы декларируют отсутствие явных и потенциальных конфликтов интересов, связанных с содержанием настоящей статьи.
Участие авторов. Мисникова И.В. — существенный вклад в концепцию и дизайн статьи; написание статьи, итоговое редактирование статьи; Золоева Д.Э. — поиск материала, написание статьи, вклад в дизайн исследования, итоговое редактирование статьи.
Все авторы одобрили финальную версию статьи перед публикацией, выразили согласие нести ответственность за все аспекты работы, подразумевающую надлежащее изучение и решение вопросов, связанных с точностью или добросовестностью любой части работы.
Список литературы
1. Lu X, Xie Q, Pan X, et al. Type 2 diabetes mellitus in adults: pathogenesis, prevention and therapy. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2024;9(1):262. Doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41392-024-01951-9
2. Zimmet P, Alberti KGMM, Stern N, et al. The Circadian Syndrome: is the Metabolic Syndrome and much more! J Intern Med. 2019;286(2):181-191. Doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/joim.12924
3. Shi Z, Tuomilehto J, Kronfeld-Schor N, et al. The circadian syndrome predicts cardiovascular disease better than metabolic syndrome in Chinese adults. J Intern Med. 2021;289(6):851-860. Doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/joim.13204
4. Poggiogalle E, Jamshed H, Peterson CM. Circadian regulation of glucose, lipid, and energy metabolism in humans. Metabolism. 2018;84:11-27. Doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.metabol.2017.11.017
5. Sakai S, Tanaka Y, Tsukamoto Y, et al. D -Alanine Affects the Circadian Clock to Regulate Glucose Metabolism in the Kidney. Kidney360. 2024;5(2):237-251. Doi: https://doi.org/10.34067/KID.0000000000000345
6. Gamble KL, Berry R, Frank SJ, Young ME. Circadian clock control of endocrine factors. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2014;10(8):466-475. Doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/nrendo.2014.78
7. Harfmann BD, Schroder EA, Esser KA. Circadian rhythms, the molecular clock, and skeletal muscle. J Biol Rhythms. 2015;30(2):84-94. Doi: https://doi.org/10.1177/0748730414561638
8. Mohawk JA, Green CB, Takahashi JS. Central and peripheral circadian clocks in mammals. Annu Rev Neurosci. 2012;35:445-462. Doi: https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-neuro-060909-153128
9. Takahashi JS, Hong HK, Ko CH, mcdearmon EL. The genetics of mammalian circadian order and disorder: implications for physiology and disease. Nat Rev Genet. 2008;9(10):764-775. Doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/nrg2430
10. den Boon FS, Sarabdjitsingh RA. Circadian and ultradian patterns of HPA-axis activity in rodents: Significance for brain functionality. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2017;31(5):445-457. Doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.beem.2017.09.001
11. Baron KG, Reid KJ. Circadian misalignment and health. Int Rev Psychiatry. 2014;26(2):139-154. Doi: https://doi.org/10.3109/09540261.2014.911149
12. Li W, Wang Z, Cao J, Dong Y, Chen Y. Perfecting the Life Clock: The Journey from PTO to TTFL. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(3):2402. Doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24032402
13. Сорокин М.Ю., Пинхасов Б.Б., Селятицкая В.Г. Циркадный ритм углеводного обмена в норме и при патологии // Acta Biomedica Scientifica. — 2023. — Т. 8. — №2. — С. 124-137. Doi: https://doi.org/10.29413/ABS.2023-8.2.12
14. Hudec M, Dankova P, Solc R, et al. Epigenetic Regulation of Circadian Rhythm and Its Possible Role in Diabetes Mellitus. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(8):3005. Doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21083005
15. Cheng H, Zhong D, Tan Y, et al. Advancements in research on the association between the biological CLOCK and type 2 diabetes. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024;15:1320605. Doi: https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2024.1320605
16. Miyamoto Y, Sancar A. Vitamin B2-based blue-light photoreceptors in the retinohypothalamic tract as the photoactive pigments for setting the circadian clock in mammals. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1998;95(11):6097-6102. Doi: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.95.11.6097
17. Institute of Medicine (US) Committee on Sleep Medicine and Research. Sleep Disorders and Sleep Deprivation: An Unmet Public Health Problem. / Ed. By Colten HR, Altevogt BM, editors. National Academies Press (US); Washington (DC): 2006
18. Vieira E, Merino B, Quesada I. Role of the clock gene Rev-erbα in metabolism and in the endocrine pancreas. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2015;17(Suppl 1):106-114. Doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/dom.12522
19. Walker WH, Hecmarie MF, Becker-Krail O, et al. Biological Clocks and Immune Function. In: Konsman, J.P., Reyes, T.M. (eds) Neuroendocrine-Immune System Interactions. Masterclass in Neuroendocrinology. 2023;13. Doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-21358-8_11
20. Stenvers DJ, Scheer FAJL, Schrauwen P, et al. Circadian clocks and insulin resistance. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2019;15(2):75-89. Doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41574-018-0122-1
21. Jakubowicz D, Wainstein J, Tsameret S, Landau Z. Role of High Energy Breakfast «Big Breakfast Diet» in Clock Gene Regulation of Postprandial Hyperglycemia and Weight Loss in Type 2 Diabetes. Nutrients. 2021;13(5):1558. Doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13051558
22. Morris CJ, Yang JN, Garcia JI, et al. Endogenous circadian system and circadian misalignment impact glucose tolerance via separate mechanisms in humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015;112(17):E2225-E2234. Doi: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1418955112
23. Saad A, Dalla Man C, Nandy DK, et al. Diurnal pattern to insulin secretion and insulin action in healthy individuals. Diabetes. 2012;61(11):2691-2700. Doi: https://doi.org/10.2337/db11-1478
24. Boden G, Ruiz J, Urbain JL, Chen X. Evidence for a circadian rhythm of insulin secretion. Am J Physiol. 1996;271(2 Pt 1):E246-E252. Doi: https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpendo.1996.271.2.E246
25. Adam EK, Quinn ME, Tavernier R, et al. Diurnal cortisol slopes and mental and physical health outcomes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2017;83:25-41. Doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psyneuen.2017.05.018
26. Morais JBS, Severo JS, Beserra JB, et al. Association Between Cortisol, Insulin Resistance and Zinc in Obesity: a Mini-Review. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2019;191(2):323-330. Doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-018-1629-y
27. Gómez-Abellán P, Díez-Noguera A, Madrid JA, Luján JA, Ordovás JM, Garaulet M. Glucocorticoids affect 24 h clock genes expression in human adipose tissue explant cultures. Plos One. 2012;7(12):e50435. Doi: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0050435
28. bahammam AS, Pirzada A. Timing Matters: The Interplay between Early Mealtime, Circadian Rhythms, Gene Expression, Circadian Hormones, and Metabolism-A Narrative Review. Clocks Sleep. 2023;5(3):507-535. Doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/clockssleep5030034
29. Xiao Q, Bauer C, Layne T, Playdon M. The association between overnight fasting and body mass index in older adults: the interaction between duration and timing. Int J Obes (Lond). 2021;45(3):555-564. Doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41366-020-00715-z
30. Chawla S, Beretoulis S, Deere A, Radenkovic D. The Window Matters: A Systematic Review of Time Restricted Eating Strategies in Relation to Cortisol and Melatonin Secretion. Nutrients. 2021;13(8):2525. Doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13082525
31. Vasey C, mcbride J, Penta K. Circadian Rhythm Dysregulation and Restoration: The Role of Melatonin. Nutrients. 2021;13(10):3480. Doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13103480
32. Hudec M, Dankova P, Solc R, et al. Epigenetic Regulation of Circadian Rhythm and Its Possible Role in Diabetes Mellitus. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(8):3005. Doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21083005
33. Buonfiglio D, Parthimos R, Dantas R, et al. Melatonin Absence Leads to Long-Term Leptin Resistance and Overweight in Rats. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2018;9:122. Doi: https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2018.00122
34. Peng F, Li X, Xiao F, Zhao R, Sun Z. Circadian clock, diurnal glucose metabolic rhythm, and dawn phenomenon. Trends Neurosci. 2022;45(6):471-482. Doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tins.2022.03.010
35. Serin Y, Acar Tek N. Effect of Circadian Rhythm on Metabolic Processes and the Regulation of Energy Balance. Ann Nutr Metab. 2019;74(4):322-330. Doi: https://doi.org/10.1159/000500071
36. Davis R, Rogers M, Coates AM, et al. The Impact of Meal Timing on Risk of Weight Gain and Development of Obesity: a Review of the Current Evidence and Opportunities for Dietary Intervention. Curr Diab Rep. 2022;22(4):147-155. Doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11892-022-01457-0
37. Garaulet M, Gómez-Abellán P. Timing of food intake and obesity: a novel association. Physiol Behav. 2014;134:44-50. Doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physbeh.2014.01.001
38. Palomar-Cros A, Srour B, Andreeva VA, et al. Associations of meal timing, number of eating occasions and night-time fasting duration with incidence of type 2 diabetes in the nutrinet-Santé cohort. Int J Epidemiol. 2023;52(5):1486-1497. Doi: https://doi.org/10.1093/ije/dyad081
39. Nas A, Mirza N, Hägele F, et al. Impact of breakfast skipping compared with dinner skipping on regulation of energy balance and metabolic risk. Am J Clin Nutr. 2017;105(6):1351-1361. Doi: https://doi.org/10.3945/ajcn.116.151332
40. Peschke E, Peschke D, Hammer T, Csernus V. Influence of melatonin and serotonin on glucose-stimulated insulin release from perifused rat pancreatic islets in vitro. J Pineal Res. 1997;23(3):156-163. Doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-079x.1997.tb00349.x
41. Damiola F, Le Minh N, Preitner N, et al. Restricted feeding uncouples circadian oscillators in peripheral tissues from the central pacemaker in the suprachiasmatic nucleus. Genes Dev. 2000;14(23):2950-2961. Doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.183500
42. Kohsaka A, Laposky AD, Ramsey KM, et al. High-fat diet disrupts behavioral and molecular circadian rhythms in mice. Cell Metab. 2007;6(5):414-421. Doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2007.09.006
43. Akbar Z, Shi Z. Dietary Patterns and Circadian Syndrome among Adults Attending NHANES 2005-2016. Nutrients. 2023;15(15):3396. Doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15153396
44. Zisapel N. New perspectives on the role of melatonin in human sleep, circadian rhythms and their regulation. Br J Pharmacol. 2018;175(16):3190-3199. Doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/bph.14116
45. van der Velde JHP, Rutters F, Rosendaal FR, et al. Associations between chronotype waist circumference, visceral fat, liver fat, and incidence of type 2 diabetes. 60th EASD Annual Meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes [abstract]. 2024;283:S146. Doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00125-024-06226-0
46. Kudielka BM, Federenko IS, Hellhammer DH, Wüst S. Morningness and eveningness: the free cortisol rise after awakening in «early birds» and «night owls». Biol Psychol. 2006;72(2):141-146. Doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsycho.2005.08.003
47. Нелаева Ю.В., Рымар О.Д., Петров И.М., и др. Роль индивидуальной организации суточных ритмов в формировании нарушений углеводного обмена // Сахарный диабет. — 2023. — Т. 26. — №3. — С. 224-235. Doi: https://doi.org/10.14341/DM12909
48. Karlsson B. Commentary: Metabolic syndrome as a result of shift work exposure?. Int J Epidemiol. 2009;38(3):854-855. Doi: https://doi.org/10.1093/ije/dyp190
49. De Bacquer D, Van Risseghem M, Clays E, et al. Rotating shift work and the metabolic syndrome: a prospective study. Int J Epidemiol. 2009;38(3):848-854. Doi: https://doi.org/10.1093/ije/dyn360
50. Knutsson A. Health disorders of shift workers. Occup Med (Lond). 2003;53(2):103-108. Doi: https://doi.org/10.1093/occmed/kqg048
51. White AJ, Kresovich JK, Xu Z, et al. Shift work, DNA methylation and epigenetic age. Int J Epidemiol. 2019;48(5):1536-1544. Doi: https://doi.org/10.1093/ije/dyz027
52. Cedernaes J, Schönke M, Westholm JO, et al. Acute sleep loss results in tissue-specific alterations in genome-wide DNA methylation state and metabolic fuel utilization in humans. Sci Adv. 2018;4(8):eaar8590. Doi: https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.aar8590
53. Fatima N, Rana S. Metabolic implications of circadian disruption. Pflugers Arch. 2020;472(5):513-526. Doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-020-02381-6
54. Hariri A, Mirian M, Zarrabi A, et al. The circadian rhythm: an influential soundtrack in the diabetes story. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023;14:1156757. Doi: https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2023.1156757
55. Engin A. Circadian Rhythms in Diet-Induced Obesity. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;960:19-52. Doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-48382-5_2
56. Meng X, Li Y, Li S, et al. Dietary Sources and Bioactivities of Melatonin. Nutrients. 2017;9(4):367. Doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/nu9040367
57. Sutanto CN, Loh WW, Kim JE. The impact of tryptophan supplementation on sleep quality: a systematic review, meta-analysis, and meta-regression. Nutr Rev. 2022;80(2):306-316. Doi: https://doi.org/10.1093/nutrit/nuab027
58. Surme S, Ergun C, Gul S, et al. TW68, cryptochromes stabilizer, regulates fasting blood glucose levels in diabetic ob/ob and high fat-diet-induced obese mice. Biochem Pharmacol. 2023;218:115896. Doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2023.115896
59. Barnea M, Haviv L, Gutman R, et al. Metformin affects the circadian clock and metabolic rhythms in a tissue-specific manner. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012;1822(11):1796-1806. Doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbadis.2012.08.005
60. Vieira E, Marroquí L, Figueroa AL, et al. Involvement of the clock gene Rev-erb alpha in the regulation of glucagon secretion in pancreatic alpha-cells. Plos One. 2013;8(7):e69939. Doi: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0069939
61. Alex A, Luo Q, Mathew D, Di R, Bhatwadekar AD. Metformin Corrects Abnormal Circadian Rhythm and Kir4.1 Channels in Diabetes. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2020;61(6):46. Doi: https://doi.org/10.1167/iovs.61.6.46
62. Yang SC, Tseng HL, Shieh KR. Circadian-clock system in mouse liver affected by insulin resistance. Chronobiol Int. 2013;30(6):796-810. Doi: https://doi.org/10.3109/07420528.2013.766204
63. Fedchenko T, Izmailova O, Shynkevych V, et al. PPAR-γ Agonist Pioglitazone Restored Mouse Liver mrna Expression of Clock Genes and Inflammation-Related Genes Disrupted by Reversed Feeding. PPAR Res. 2022;2022:7537210. Doi: https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/7537210
Об авторах
И. В. МисниковаРоссия
Мисникова Инна Владимировна - д.м.н.; ScopusAuthor ID: 559756; eLibrary SPIN: 3614-3011.
Москва
Конфликт интересов:
Авторы декларируют отсутствие явных и потенциальных конфликтов интересов, связанных с содержанием настоящей статьи
Д. Э. Золоева
Россия
Золоева Дзерасса Эльбрусовна
129110, Москва, ул. Щепкина, д. 61/2
Конфликт интересов:
Авторы декларируют отсутствие явных и потенциальных конфликтов интересов, связанных с содержанием настоящей статьи
Дополнительные файлы
|
|
1. Рисунок 1. Схематическое изображение молекулярной структуры циркадных часов (адаптировано из работы Vieira и соавт., 2015 г.) [18]. | |
| Тема | ||
| Тип | Исследовательские инструменты | |
Посмотреть
(373KB)
|
Метаданные ▾ | |
|
|
2. Рисунок 2. Метаболические процессы, подверженные циркадной регуляции (адаптировано из работы Stenvers и соавт., 2019 г.) [20]. | |
| Тема | ||
| Тип | Исследовательские инструменты | |
Посмотреть
(1MB)
|
Метаданные ▾ | |
Рецензия
Для цитирования:
Мисникова И.В., Золоева Д.Э. Влияние циркадных ритмов на углеводный обмен в норме и при сахарном диабете. Сахарный диабет. 2025;28(4):367-375. https://doi.org/10.14341/DM13241
For citation:
Misnikova I.V., Zoloeva D.E. The influence of circadian rhythms on carbohydrate metabolism in health and in diabetes mellitus. Diabetes mellitus. 2025;28(4):367-375. (In Russ.) https://doi.org/10.14341/DM13241

Контент доступен под лицензией Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0).















































