Перейти к:
Ожирение у больных сахарным диабетом 1 типа: причины и следствия
https://doi.org/10.14341/DM13237
Аннотация
Ожирение у больных сахарным диабетом 1 типа (СД1) становится все более важной проблемой диабетологии. По данным разных исследований, распространенность избыточной массы тела и ожирения среди пациентов с СД1 варьирует от 15 до 50%. Около четверти больных СД1 имеют метаболический синдром. С одной стороны, увеличение массы тела у пациентов с СД1 отражает общепопуляционный тренд. С другой стороны, увеличению массы тела способствуют факторы, специфичные для диабета, такие как базис-болюсная инсулинотерапия, хроническая передозировка инсулина, гипогликемии, а также психологические проблемы, связанные с заболеванием. Связь СД1 и ожирения может быть двунаправленной. Установлено, что избыточная масса тела и ожирение повышают риск развития СД1, вероятно, способствуя аутоиммунной деструкции бета-клеток. Лица с избыточной массой тела и ожирением, по сравнению с больными с нормальной массой тела, чаще имеют инсулинорезистентность, дислипидемию и нуждаются в более высоких дозах инсулина для достижения целевых параметров гликемического контроля. Ожирение у лиц с СД1 является фактором риска диабетических микроангиопатий, артериальной гипертензии, хронической болезни почек, хронической сердечной недостаточности, сердечно-сосудистых событий, неалкогольной жировой болезни печени и ассоциировано с повышенной смертностью. Следовательно, поддержание нормальной массы тела следует считать важной задачей при лечении СД1. Обучение, диета с умеренным ограничением калорий и физическая активность являются основой стратегии профилактики и лечения ожирения у лиц с СД1. В качестве перспективных терапевтических опций рассматриваются агонисты глюкагон-подобного пептида-1, двойные агонисты глюкагон-подобного пептида-1 и глюкозозависимого инсулинотропного полипептида, ингибиторы глюкозо-натриевого котранспортера-2, метформин, однако данных по эффективности и безопасности применения этих лекарств при СД1 пока недостаточно. Накапливается опыт выполнения бариатрических вмешательств у лиц с СД1 и морбидным ожирением. Дальнейшие исследования необходимы для создания программ профилактики и лечения ожирения у пациентов с СД1.
Ключевые слова
Для цитирования:
Климонтов В.В., Юшин А.Ю. Ожирение у больных сахарным диабетом 1 типа: причины и следствия. Сахарный диабет. 2025;28(4):394-403. https://doi.org/10.14341/DM13237
For citation:
Klimontov V.V., Yushin A.Yu. Obesity in Patients with Type 1 Diabetes: Causes and Consequences. Diabetes mellitus. 2025;28(4):394-403. (In Russ.) https://doi.org/10.14341/DM13237
Сахарный диабет 1 типа (СД1) — одно из наиболее серьезных эндокринных заболеваний, которым в мире страдает более 8,7 млн человек [1]. В России, как и во многих странах мира, наблюдается рост распространенности СД1 [2]. Все больше данных свидетельствует о гетерогенности СД1 и возможном изменении его клинического течения. В последние годы значительная часть новых случаев СД1 стала регистрироваться у взрослых людей [1]. Предложена концепция эндотипов СД1, которые различаются по эпидемиологическим, клиническим, генетическим, иммунологическим, гистологическим и метаболическим характеристикам [3]. Новой клинической реальностью стали избыточная масса тела и ожирение у лиц с СД1. В этом обзоре мы представляем данные о распространенности и факторах риска ожирения у больных СД1, анализируем влияние ожирения на метаболические параметры, развитие СД1 и его осложнений, а также обсуждаем возможности применения различных методов лечения ожирения при СД1. Поиск источников проведен в базe данных PubMed/Medline по ключевым словам type 1 diabetes И obesity ИЛИ overweight ИЛИ insulin resistance ИЛИ metabolic syndrome, дополнительный поиск — по спискам цитируемой литературы.
РАСПРОСТРАНЕННОСТЬ ИЗБЫТОЧНОЙ МАССЫ ТЕЛА И ОЖИРЕНИЯ СРЕДИ ПАЦИЕНТОВ С СД1
Распространенность ожирения и избыточной массы тела продолжает увеличиваться как в детской, так и во взрослой популяции [4]. Эта тенденция не обошла стороной и людей с СД1. Так, недавнее исследование в Бельгии, включавшее 89 834 человека с СД1 в возрасте от 1 года до 80 лет, показало, что распространенность ожирения и избыточной массы тела среди лиц с СД1 сопоставима с таковой в общей популяции [5].
Согласно исследованию, проведенному на базе шведского национального регистра диабета (NDR, N=26 125), среднее значение индекса массы тела (ИМТ) в популяции пациентов с СД1 выросло с 24,7 до 25,7 кг/м² за период с 1998 по 2012 гг. [6]. В тот же период прослежена тенденция к росту распространенности ожирения у лиц с СД1 в США: среди больных, включенных в Geisinger Health System (N=4060), распространенность ожирения увеличилась с 32,6 в 2004 г. до 36,8% в 2018 г. Распространенность ожирения среди пациентов с СД1 и у лиц без СД оказалась сопоставимой [7]. Данные крупного регистра T1D Exchange Clinic Registry (T1DX) в США по когорте пациентов, включавшей 22 697 человек с СД1, также показали отсутствие значимых различий по ИМТ между пациентами с СД1 и общей популяцией [8]. В Австрии распространенность избыточной массы тела среди пациентов с СД1 и в общей популяции составила 39,8% и 33,1%, распространенность ожирения — 14% и 13,1% cоответственно [9]. В недавней работе из Бельгии, при сравнении данных по 26 791 пациенту за 2001 и 2022 гг., зафиксирован почти двукратный рост распространенности ожирения среди лиц с СД1 (с 12,1% в 2001 г. до 21,7% в 2022 г.) [10].
В ряде исследований оценивалась распространенность избыточной массы и ожирения среди детей и подростков с СД1. Анализ данных регистра T1DX в США зафиксировал наличие избыточной массы тела у 22,9% подростков с СД1 в возрасте от 13 до 18 лет, распространенность ожирения в этой группе составила 13,1% [11]. Анализ базы данных Diabetes Patienten Verlaufsdokumentation (DPV) показал более благоприятную обстановку в отношении распространенности ожирения у детей с СД1 в Германии и Австрии (2,8%), число детей с избыточной массой тела составило 12,5% [12]. В исследовании SWEET (Better control in Pediatric and Adolescent diabetes: Working to crEate CEnTers of Reference), включавшем 23 026 детей от 2 до 18 лет с СД1 из разных стран мира, ожирение и избыточная масса тела зафиксированы у 31,8% пациентов [13].
Согласно результатам метаанализа 27 исследований, включавших в общей сложности 45 811 пациентов, распространенность метаболического синдрома (МС) при СД1 составляет 23,7%. Распространенность МС при оценке за периоды 2005–2014 гг. и 2015–2020 гг. выросла с 21,8 до 26,6% [14].
Таким образом, проблема избыточной массы тела и ожирения затрагивает существенную часть детей и взрослых с СД1. Рост массы тела среди больных СД1 отражает такую же тенденцию в общей популяции.
ФАКТОРЫ РИСКА РАЗВИТИЯ ОЖИРЕНИЯ ПРИ СД1
Общепопуляционные факторы риска (переедание, гиподинамия и др.), несомненно, играют роль в развитии ожирения и при СД1. Однако пациенты с СД1 встречаются с рядом особых вызовов в поддержании массы тела. Важнейшим вызовом является инсулинотерапия. Уже в первые годы клинического применения инсулина, заметив его анаболический эффект, клиницисты пытались применять гормон «с целью откармливания» в самых разных ситуациях, от базедовой болезни и нарушений питания до онкологических заболеваний [15]. В исследовании DCCT/EDIC (Diabetes Control and Complications Trial / Epidemiology of Diabetes Interventions and Complications) было доказано, что интенсификация инсулинотерапии способствует набору массы тела [16]. Механизм увеличения массы тела на фоне инсулинотерапии включает прямой анаболический эффект инсулина на синтез липидов. Лечение инсулином до сих пор остается не вполне физиологичным: при подкожном введении инсулин сразу поступает в системный кровоток, минуя печень. Таким образом, происходит дисбаланс между печеночными и периферическими эффектами инсулина, формируется периферическая гиперинсулинемия, которая способствует накоплению жира [17]. Исчезновение глюкозурии вносит вклад в положительный энергетический баланс при назначении инсулина или интенсификации инсулинотерапии.
Гипогликемия и страх гипогликемии также являются фактором риска увеличения массы тела при лечении инсулином. Купирование гипогликемии требует дополнительного приема углеводов, как правило, рафинированных. Это формирует нездоровые пищевые привычки у ряда больных. Особой проблемой является вечернее переедание из-за страха ночной гипогликемии. Страх гипогликемии заставляет некоторых пациентов отказываться от физических нагрузок или принимать избыточное количество углеводов перед или во время нагрузки [18], что также способствует развитию ожирения.
Инсулинотерапия, будучи одним из триггеров увеличения массы тела, способна запускать порочный круг. За набором массы тела следует снижение чувствительности к инсулину, что, в свою очередь, приводит к увеличению доз экзогенного гормона и дальнейшему увеличению веса [19]. При СД1 положительные ассоциации между дозами инсулина и ИМТ выявлены у взрослых [20–22], детей [23] и подростков [11].
Сообщалось о более высоком коэффициенте стандартного отклонения ИМТ у подростков на постоянной подкожной инфузии инсулина в сравнении со сверстниками на режиме многократных инъекций [24]. Оценив динамику массы тела на помповой инсулинотерапии у 5133 пациентов с СД1 в возрасте до 20 лет, Tauschmann M. и соавт. выделили различные траектории изменений: почти у половины пациентов (49%) наблюдалось повышение коэффициента стандартного отклонения ИМТ, у 12% показатель не изменился, а у 39% наблюдалось снижение. Изменения ИМТ сочетались с разнонаправленными изменениями уровня гликированного гемоглобина (HbA1c) и дозы инсулина [25]. По-видимому, для поддержания нормальной массы тела важен не столько режим инсулинотерапии (помпа или инъекции), сколько его правильная адаптация к питанию и физической активности.
Роль диетических и психосоциальных факторов в развитии ожирения на фоне СД1 недостаточно изучена. В ряде работ отмечена ассоциация между количеством потребляемого жира с пищей и ИМТ у пациентов СД1 [26][27]. По некоторым данным, нарушения пищевого поведения (в том числе нервная булимия и психогенное переедание) у подростков с СД1 встречаются в два раза чаще, чем у здоровых [28]. Развитию нарушений пищевого поведения и ожирения могут способствовать высокий уровень стресса, связанного с заболеванием, депрессия [29], недостаточная поддержка со стороны окружающих, низкий уровень самооценки [30]. Эти нарушения и диетические ограничения ассоциированы с более высоким содержанием жира в организме [31]. В исследовании SEARCH (2156 человек от 10 до 25 лет) ИМТ был значительно выше у пациентов, пропускавших приемы пищи, у склонных к компульсивному перееданию, а также у тех, кто пытался ограничивать введение инсулина [32]. Механизмы нарушения регуляции пищевого поведения у больных СД1 требуют дальнейших исследований.
Имеются свидетельства, что недостаточная продолжительность определенных фаз сна (а именно, фазы REM) у подростков с СД1 ассоциирована с ожирением [33]. Прерывистость сна может быть обусловлена необходимостью замера уровня глюкозы или гипогликемией.
Таким образом, риск ожирения при СД1 связан как с общепопуляционными, так и со специфичными для заболевания факторами (табл. 1). Причины и механизмы увеличения массы тела могут различаться у разных больных.
Таблица 1. Факторы риска развития ожирения у больных сахарным диабетом 1 типа
|
Общепопуляционные |
Связанные с заболеванием |
|
• Высокая калорийность пищи • Гиподинамия • Генетическая предрасположенность • Психосоциальные факторы (нарушения пищевого поведения, стресс, депрессия) • Возраст |
• Базис-болюсная инсулинотерапия • Хроническая передозировка инсулина • Гипогликемии • Страх гипогликемии • Психосоциальные факторы (стресс, связанный с заболеванием, низкий уровень социальной поддержки) |
ОЖИРЕНИЕ И СД1: ЧТО ПЕРВИЧНО?
В 2001 г. T.J. Wilkin опубликовал казавшуюся провокационной теорию, названную «гипотезой акселераторов». Она предполагала, что оба основных типа СД имеют сходные механизмы развития и различаются степенью потери бета-клеток и степенью воздействия «акселераторов», к числу которых относится инсулинорезистентность. Обусловленная избыточным весом и гиподинамией, инсулинорезистентность усиливает апоптоз бета-клеток и ускоряет развитие обоих типов СД [34].
В последние годы интерес к роли ожирения в развитии СД1 существенно возрос. Недавний метаанализ 10 наблюдательных исследований, включавших в общей сложности около 1,7 миллиона человек, подтвердил ассоциацию между массой тела и риском развития СД1. Согласно результатам этого метаанализа, наличие избыточной массы тела повышает риск СД1 в 1,35 раза, наличие ожирения — в 2,17 раза [35]. Исследование с использованием Менделевской рандомизации показало причинно-следственную связь между генетической предрасположенностью к ожирению и аутоимунными заболеваниями, включая СД1 [36].
Механизмы вовлечения ожирения в развитие СД1 обсуждаются в литературе. Инсулинорезистентность является одним из наиболее очевидных патогенетических факторов. Предполагают также, что повышение концентрации насыщенных жирных кислот при ожирении может негативно влиять на состояние бета-клеток («липотоксичность»). Хроническое системное воспаление с повышением продукции провоспалительных цитокинов и нарушение микрофлоры кишечника, свойственные ожирению, могут способствовать развитию аутоиммунной деструкции бета-клеток или повышать уязвимость бета-клеток к аутоиммунной агрессии [37][38]. Клинические данные подтверждают эти предположения. В проспективном исследовании TrialNet повышенный ИМТ увеличивал вероятность усугубления аутоиммунного процесса (появления трех видов антител к антигенам островков) у детей с высоким риском развития СД1 [39].
Показано, что величина набора массы тела в первый год после постановки диагноза у детей с СД1 отрицательно коррелирует с длительностью ремиссии заболевания [40]. У детей с более высоким ИМТ уровень С-пептида в момент постановки диагноза СД1 выше, однако в последующие 2 года падение С-пептида происходит более быстрыми темпами [41]. Можно предполагать, что ожирение не только является фактором риска развития СД1, но и ускоряет прогрессирование заболевания.
Таким образом, связь ожирения с СД1 может носить двунаправленный характер. Патогенетические механизмы, лежащие в основе взаимосвязи двух заболеваний, нуждаются в дальнейших исследованиях.
ИНСУЛИНОРЕЗИСТЕНТНОСТЬ И МЕТАБОЛИЧЕСКИЕ НАРУШЕНИЯ У ПАЦИЕНТОВ С СД1 И ОЖИРЕНИЕМ
Исследования с эугликемическим гиперинсулинемическим клэмпом — золотым стандартом в оценке чувствительности к инсулину показали, что инсулинорезистентность не является редкостью у больных СД1, хотя данные об ассоциации инсулинорезистентности с ИМТ противоречивы [42][43]. Учитывая трудоемкость клэмп-методов, в последние годы для оценки чувствительности к инсулину у больных СД1 чаще применяют суррогатные индексы, в частности, расчетную скорость утилизации глюкозы (рСУГ, англ. estimated glucose disposal rate). Данный параметр рассчитывают на основе окружности талии, уровня HbA1c, наличия артериальной гипертензии [44]. Установлено, что у лиц с СД1 рСУГ снижается в ряду: нормальная масса тела — избыточная масса тела — ожирение, при этом параметр обратно ассоциирован с ИМТ, окружностью талии, массой жировой ткани на туловище [45] и процентом висцерального жира [46]. Сниженная рСУГ является фактором риска МС у пациентов с СД1 в возрасте 10 лет и старше [46]. Отношение окружности талии к росту, как и окружность талии, у больных СД1 также являются непрямыми маркерами инсулинорезистентности [47].
Наличие ожирения может оказывать влияние на качество контроля гликемии. В ряде исследований у пациентов с СД1 и ожирением зафиксирован более высокий средний уровень гликемии (при оценке по HbA1c), чем у больных с нормальной массой тела [22][48–50]. Некоторые авторы не выявили такой связи [51]. В двух недавних исследованиях оценивалась связь параметров непрерывного мониторинга глюкозы с чувствительностью к инсулину у больных СД1 [45][52]. В обоих исследованиях зафиксирована связь между уменьшением чувствительности к инсулину (по рСУГ) и увеличением времени в диапазоне выше целевого, а также с уменьшением времени в целевом диапазоне. В одном исследовании [45] пациенты с ИМТ>25 кг/м² имели меньший показатель времени в диапазоне гипогликемии (<3 ммоль/л), меньшее число эпизодов низкого уровня глюкозы и меньшие показатели вариабельности гликемии (скорость изменений уровня глюкозы, индекс лабильности) по сравнению с пациентами с нормальным весом. Снижение вариабельности гликемии было ассоциировано с уменьшением чувствительности к инсулину.
Больные СД1 с ожирением чаще имеют дислипидемию, чем пациенты с нормальной массой тела [49][51]. Наличие ожирения ассоциировано с более высокими уровнями триглицеридов и холестерина липопротеинов низкой плотности, как у взрослых пациентов [22][51], так и у детей и подростков с СД1 [50].
Таким образом, избыточная масса тела и ожирение у лиц с СД1 сопряжены с инсулинорезистентностью и дислипидемией. Хотя пациенты с СД1 и ожирением могут иметь более низкую вариабельность гликемии и меньший риск гипогликемии, целевые показатели гликемического контроля у них достигаются реже и обычно требуют применения более высоких доз инсулина.
ВЛИЯНИЕ ОЖИРЕНИЯ И РЕЗИСТЕНТНОСТИ К ИНСУЛИНУ НА РИСК РАЗВИТИЯ ОСЛОЖНЕНИЙ И СМЕРТНОСТЬ БОЛЬНЫХ СД1
Анализ данных исследования DCCT и его наблюдательной пост-фазы EDIC показал, что благоприятный эффект интенсификации инсулинотерапии на факторы сердечно-сосудистого риска у больных СД1 нивелируется, если улучшение гликемического контроля сопровождается значительным увеличением массы тела [16].
Накопленные к настоящему времени данные свидетельствуют, что ожирение у больных СД1 ассоциировано с артельной гипертензией и повышенным риском микрососудистых и макрососудистых осложнений (табл. 2). В крупных когортных исследованиях артериальная гипертензия чаще встречалась в группе пациентов с СД1 и ожирением [49][51][53]. Установлено, что наличие избыточной массы тела у пациентов с СД1 повышает риск развития артериальной гипертензии в 1,7 раза, ожирение повышает этот риск в 3,2 раза [54]. Имеются данные об ассоциации ожирения с более высоким риском диабетической ретинопатии [49][53][55], нефропатии [7][49][51][55], нейропатии и макрососудистых осложнений [49][53][55], а также хронической сердечной недостаточности [56]. Анализ данных шведского регистра NDR показал, что больные СД1 с ИМТ≥25 кг/м² имеют более высокий риск сердечно-сосудистых катастроф, хронической сердечной недостаточности и смерти, чем больные с нормальной массой тела [6].
Таблица 2. Ассоциации индекса массы тела, метаболического синдрома и инсулинорезистентности с риском развития осложнений у больных сахарным диабетом 1 типа
|
Исследование |
Страна |
Кол-во пациентов (п) |
Возраст |
Дизайн |
Основной результат |
|
Giandalia A. et al. [49] |
Италия |
37 436 |
>18 лет (49,6 лет) |
КС |
Хроническая болезнь почек, диабетическая ретинопатия и сердечно-сосудистые заболевания более распространены в группе больных с ожирением |
|
Genua I. et al. [51] |
Испания |
6068 |
≥18 лет (48,7±15,9) |
КС |
Хроническая болезнь почек чаще наблюдается у больных с ожирением |
|
Wallace A.S. et al. 2022 [7] |
США |
4060 |
≥18 лет |
КС |
Риск хронической болезни почек ассоциирован с ожирением |
|
Moosaie F. et al. [55] |
Иран |
10 641 |
>1 года–99 лет |
КС |
Ожирение ассоциировано с микро- и макрососудистыми осложнениями, нейропатией |
|
Lee A.S. et al. [62] |
Австралия |
6195 |
≥18 лет (44,3±15,6) |
КС |
Метаболический синдром ассоциирован с микро- и макрососудистыми осложнениями, нейропатией |
|
Lalanne-Mistri M-L. et al. [53] |
Канада |
1091 |
44,4±15 лет |
КС |
Ожирение ассоциировано с более высоким риском нейропатии, ретинопатии, макрососудистых осложнений |
|
Lavens A. et al. [10] |
Бельгия |
26 791 |
≥16 лет |
КС |
Ожирение и метаболический синдром ассоциированы с более высоким риском ретинопатии, хронической болезни почек, нейропатии и макрососудистых осложнений |
|
Edqvist J. et al. [6] |
Швеция |
26 125 |
33,3±13 лет |
П |
Повышение ИМТ ассоциировано с повышением риска смерти от сердечно-сосудистых заболеваний и от всех причин, госпитализациями по поводу хронической сердечной недостаточности |
|
Parente E.B. et al. [56] |
Финляндия |
4668 |
≥18 лет |
П |
Абдоминальное ожирение ассоциировано с риском госпитализации и смерти по причине хронической сердечной недостаточности |
|
Garofolo M. et al. [51] |
Италия |
736 |
40,2 ±11,7 года |
П |
Инсулинорезистентность ассоциирована с сердечно-сосудистыми заболеваниями, ишемической болезнью сердца и смертностью от всех причин |
Дизайн исследований: КС — кросс-секционное, П — проспективное.
Резистентность к инсулину у больных СД1 также ассоциирована с риском сосудистых осложнений. В частности, показано, что более низкая рСУГ ассоциирована с микроангиопатиями [57]. По данным проспективного 10-летнего исследования [58], сниженная чувствительность к инсулину (установленная по рСУГ) является предиктором ишемической болезни сердца, сердечно-сосудистых событий и общей смертности у больных СД1. Метаанализ 8 исследований, включавших в общей сложности 21 930 пациентов с СД1, показал наличие ассоциации между резистентностью к инсулину (сниженной рСУГ) и риском сердечно-сосудистых заболеваний, а также смертностью от всех причин [59]. Наличие инсулинорезистентности у больных СД1 ассоциировано с неалкогольной жировой болезнью печени [60]. Последняя, в свою очередь, показала связь с диабетической ретинопатией и хронической болезнью почек [61].
Проведенное в Австралии крупное кросс-секционное исследование (N=6195) выявило ассоциации МС с осложнениями СД1. Вероятность развития ретинопатии, терминальной стадии хронической болезни почек, нейропатии и макрососудистых осложнений была в 2–3 раза выше у пациентов с СД1, имеющих МС, в сравнении с больными без МС. Распространенность МС повышалась с возрастом, при этом связь МС с макроваскулярными осложнениями была более выраженной у больных СД1 до 40 лет [62].
Таким образом, ожирение у больных СД1 является фактором риска микрососудистых осложнений, хронической болезни почек, артериальной гипертензии, МС, хронической сердечной недостаточности, сердечно-сосудистых заболеваний, неалкогольной жировой болезни печени, и ассоциировано с повышением смертности (рис. 1). Очевидно, что поддержание нормальной массы тела должно быть частью терапевтической стратегии при СД1.
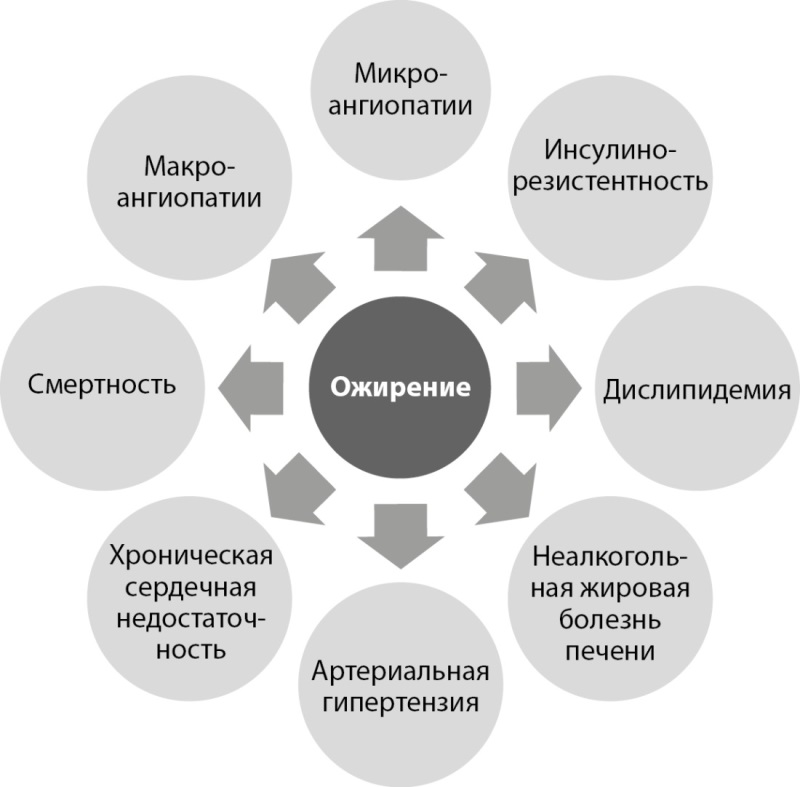
Рисунок 1. Ожирение как фактор риска осложнений и неблагоприятных исходов при сахарном диабете 1 типа.
ТЕРАПЕВТИЧЕСКИЕ ПОДХОДЫ К ВЕДЕНИЮ БОЛЬНЫХ СД1 С ОЖИРЕНИЕМ
Изокалорийное сбалансированное питание с адаптацией углеводов и дозы инсулина является основой профилактики ожирения у больных СД1. Однако специальных исследований, посвященных влиянию различных диет на массу тела и метаболические параметры у пациентов с СД1 и ожирением, очень мало. В недавнем рандомизированном клиническом исследовании (РКИ) ACT1ON (Advancing Care for Type 1 Diabetes and Obesity Network) оценивался эффект различных диетических вмешательств на вес и углеводный обмен у молодых (19–30 лет) больных СД1 с ИМТ 27–39,9 кг/м². В процессе исследования участники были рандомизированы на три группы. Первая группа придерживалась гипокалорийной низкоуглеводной диеты (1200–1800 ккал/сут, доля углеводов 20–25% в суточной калорийности, доля насыщенных жиров <10%), 2-я группа — гипокалорийной диеты с ограничением жиров (1200–1800 ккал/сут, доля жиров <30%, доля насыщенных жиров <10%), в 3-й группе была рекомендована средиземноморская диета без снижения калорийности. В течение трех месяцев снижение массы тела составило -2,4 (95% ДИ -3,9, -0,93), -1,3 (95% ДИ -3,4, 0,82), -2,4 (95% ДИ -4,3, -0,52) кг в 1-й, 2-й и 3-й группе соответственно, уровень HbA1c значимо снизился только во 2-й группе: -0,65% (95% ДИ -1,1, -0,18%, p=0,027). Время в диапазоне ниже целевого, рассчитанное по данным непрерывного мониторинга уровня глюкозы, было больше в группе низкоуглеводной диеты [63]. Показано, что высокая приверженность средиземноморской диете у детей с СД1 в возрасте от 6 до 18 лет ассоциирована с более высокими значениями времени в целевом диапазоне глюкозы и меньшим процентом жира в организме [64].
Физические нагрузки у лиц с СД1 не только способствуют повышению мышечной массы и уменьшению массы висцерального жира, но и улучшают чувствительность к инсулину [18]. Между тем физические нагрузки увеличивают риск гипогликемии и гипергликемии. Сталкиваясь с трудностями в управлении гликемией и другими барьерами, многие пациенты не придерживаются рекомендаций по физической активности. В результате, больные СД1 более склонны к гиподинамии, чем лица без СД [65]. В настоящее время не установлено, какие именно физические нагрузки (по виду, интенсивности, продолжительности и т.д.) являются наиболее предпочтительными для больных СД1 с ожирением. В исследовании ACT1ON физические нагрузки умеренной или высокой интенсивности оказались ассоциированы с более высоким уровнем HbA1c и временем в диапазоне выше целевого у больных СД1 с избыточной массой тела или ожирением [66]. Сами по себе физические нагрузки обладают умеренным эффектом на массу тела, поэтому должны быть дополнением к диете [67].
В последние годы обсуждается вопрос о применении метформина, препаратов инкретинового ряда, ингибиторов натрий-глюкозного котранспортера 2 типа (НГЛТ-2) для лечения больных СД1 с ожирением. Исследований, посвященных оценке эффективности и безопасности этих классов препаратов у больных СД1, не много. Метаанализ 19 исследований (1540 пациентов), в ходе которых метформин был добавлен к инсулинотерапии у больных СД1, показал, что прием метформина способствует статистически значимому снижению массы тела (-2,24 кг, ДИ -2,97, -1,51 кг, р<0,001), а также уменьшению суточных доз инсулина и жировой массы [68]. По данным другого метаанализа, объединившего результаты исследований по оценке влияния лекарственных средств и изменений образа жизни на массу тела (33 РКИ, N=9344), прием метформина не приводит к снижению веса у пациентов с СД1. При этом ингибиторы НГЛТ-2 эмпаглифлозин и сотаглифлозин способствовали снижению массы тела. Среднее уменьшение массы тела при приеме эмпаглифлозина в дозе 10 мг и 25 мг составило 2,7 (95% ДИ -3,24, -2,31) и 3,06 (95% ДИ -3,57, -2,55) кг соответственно [69]. Следует помнить, что применение ингибиторов НГЛТ-2 у больных СД1 увеличивает риск кетоацидоза, что требует мониторинга кетоновых тел в ходе лечения [70].
Наиболее значимые результаты по влиянию на массу тела получены при лечении препаратами инкретинового ряда. В РКИ Lira Pump Trial применение агониста глюкагонодобного пептида-1 (арГПП-1) лираглутида в дозе 1,8 мг/сут у больных СД1 с избыточной массой тела или ожирением на помповой инсулинотерапии обеспечило снижение массы тела в среднем на 6,3 кг (р<0,001 в сравнении с плацебо). Это сопровождалось уменьшением уровня HbA1c на 0,5% (р<0,001) и суточной дозы инсулина на 8 ЕД (р=0,008) [71]. Garg S.K. и соавт. провели ретроспективный анализ эффективности применения тирзепатида, двойного агониста рецепторов ГПП-1 и глюкозозависимого инсулинотропного пептида (ГИП), у больных СД1 с избыточной массой тела или ожирением. Лечение тирзепатидом в течение года сопровождалось снижением ИМТ (в среднем на 18,5%, р<0,0001), уровня HbA1c (на 0,67%, р=0,004) и суточной дозы инсулина (на 22,8 ЕД, р=0,0006) [72].
Edwards K. и соавт. сравнили результаты применения арГПП-1 и ингибиторов НГЛТ-2 у больных СД1 в реальной клинической практике. После года терапии у пациентов, получавших арГПП-1, наблюдалось значимое снижение массы тела (в среднем на 5,1 кг, р<0,001), HbA1c (на 0,4%, р=0,007) и общей суточной дозы инсулина (на 19,9 ЕД, р<0,001). У больных на терапии ингибиторами НГЛТ-2 зафиксировано снижение уровня HbA1c (на 0,6%; р<0,001) и дозы базального инсулина (на 5,7 ЕД, р=0,003). Уменьшение массы тела было более выраженным на терапии арГПП-1, чем на ингибиторах НГЛТ-2 (р=0,027). Диабетический кетоацидоз ожидаемо чаще наблюдался на терапии ингибиторами НГЛТ-2 [73]. Следует подчеркнуть, что все упомянутые нами препараты официально не одобрены для применения у больных СД1.
Накапливаются данные о применении бариатрической хирургии у больных СД1 с морбидным ожирением. Бариатрические операции у этой категории пациентов не только значительно уменьшают массу тела, но и способствуют снижению уровня HbA1c и потребности в инсулине [74]. Так, в одном из недавних исследований [75], через 5 лет после выполнения рукавной резекции желудка или желудочного шунтирования по Ру среднее снижение массы тела у больных СД1 составило 14,2 и 22,6% соответственно, суточная доза инсулина снизилась со 140 до 90 ЕД. Диабетический кетоацидоз и тяжелая гипогликемия — наиболее частые метаболические осложнения у пациентов с СД1 после бариатрических вмешательств [76].
Таким образом, лечение ожирения у пациентов с СД1 является довольно сложной задачей, учитывая повышенные риски диет, физических нагрузок и ряда лекарственных препаратов при данном заболевании. Препараты инкретинов и метаболическая хирургия являются перспективными методами лечения ожирения, однако их эффективность и безопасность у больных СД1 нуждаются в дальнейших исследованиях.
ЗАКЛЮЧЕНИЕ
Современный мир страдает от последствий избыточный массы тела и ожирения. Долгое время существовала недооценка проблемы избыточного веса у пациентов с СД1, однако результаты современных исследований однозначно свидетельствуют о том, что распространенность избыточной массы тела и ожирения при СД1 не ниже (а по некоторым данным даже выше), чем в общей популяции. Ожирение, будучи ассоциированным с резистентностью к инсулину, затрудняет достижение целевых параметров контроля гликемии и повышает риск развития сосудистых осложнений. Пациенты с СД1 имеют не только общепопуляционные, но и специфичные для заболевания факторы риска ожирения, такие как базис-болюсная инсулинотерапия, хроническая передозировка инсулина, гипогликемии и страх гипогликемии, а также психосоциальные факторы, связанные с заболеванием. Из-за ряда особенностей, характерных для лиц с СД1, ожирение в данной группе больных представляется уникальной медицинской проблемой, требующей разработки особых решений. В настоящее время диета и физические нагрузки являются основой стратегии по профилактике ожирения на фоне СД1. Данных об эффективности и безопасности препаратов, снижающих вес, в этой специфической группе пациентов пока недостаточно. Для создания программ профилактики и лечения ожирения у пациентов с СД1 необходимы дальнейшие исследования.
ДОПОЛНИТЕЛЬНАЯ ИНФОРМАЦИЯ
Источники финансирования. Исследование выполнено за счет госзадания НИИКЭЛ — филиал ИЦиГ СО РАН.
Конфликт интересов. Авторы декларируют отсутствие явных и потенциальных конфликтов интересов, связанных с публикацией настоящей статьи.
Участие авторов. Климонтов В.В. — концепция исследования, анализ данных, написание и редактирование текста; Юшин А.Ю. — сбор материала, анализ данных, написание текста. Оба автора одобрили финальную версию статьи перед публикацией, выразили согласие нести ответственность за все аспекты работы, подразумевающую надлежащее изучение и решение вопросов, связанных с точностью или добросовестностью любой части работы.
Список литературы
1. Ogle GD, Wang F, Gregory GA, Maniam J; T1D Index consortium. Type 1 diabetes estimates in children and adults - 2022 [cited 2024 Sep 17]. Available online: https://diabetesatlas.org/atlas/t1d-index-2022/
2. Дедов И.И., Шестакова М.В., Викулова О.К., и др. Сахарный диабет в Российской Федерации: динамика эпидемиологических показателей по данным Федерального регистра сахарного диабета за период 2010 – 2022 гг. // Сахарный диабет. — 2023. — Т. 26. — № 2. — С. 104-123doi: https://doi.org/10.14341/DM13035
3. Redondo MJ, Morgan NG. Heterogeneity and endotypes in type 1 diabetes mellitus. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2023;19(9):542-554. doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41574-023-00853-0
4. GBD 2015 Obesity Collaborators; Afshin A, Forouzanfar MH, Reitsma MB, et al. Health Effects of Overweight and Obesity in 195 Countries over 25 Years. N Engl J Med. 2017;377(1):13-27. doi: https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1614362
5. Lavens A, Nobels F, De Block C, et al. Effect of an Integrated, Multidisciplinary Nationwide Approach to Type 1 Diabetes Care on Metabolic Outcomes: An Observational Real-World Study. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2021;23(8):565-576. doi: https://doi.org/10.1089/dia.2021.0003
6. Edqvist J, Rawshani A, Adiels M, et al. BMI, Mortality, and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Type 1 Diabetes: Findings Against an Obesity Paradox. Diabetes Care. 2019;42(7):1297-1304. doi: https://doi.org/10.2337/dc18-1446
7. Wallace AS, Chang AR, Shin JI, et al. Obesity and Chronic Kidney Disease in US Adults With Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2022;107(5):1247-1256. doi: https://doi.org/10.1210/clinem/dgab927
8. Foster NC, Beck RW, Miller KM, et al. State of Type 1 Diabetes Management and Outcomes from the T1D Exchange in 2016-2018. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2019;21(2):66-72. doi: https://doi.org/10.1089/dia.2018.0384
9. Fellinger P, Fuchs D, Wolf P, et al. Overweight and obesity in type 1 diabetes equal those of the general population. Wien Klin Wochenschr. 2019;131(3-4):55-60. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00508-018-1434-9
10. Lavens A, De Block C, Oriot P, et al. Metabolic health in people living with type 1 diabetes in Belgium: a repeated cross-sectional study. Diabetologia. 2024; in press. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00125-024-06273-7
11. Minges KE, Whittemore R, Weinzimer SA, et al. Correlates of overweight and obesity in 5529 adolescents with type 1 diabetes: The T1D Exchange Clinic Registry. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2017;126:68-78. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diabres.2017.01.012
12. Fröhlich-Reiterer EE, Rosenbauer J, Bechtold-Dalla Pozza S, et al. Predictors of increasing BMI during the course of diabetes in children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes: data from the German/Austrian DPV multicentre survey. Arch Dis Child. 2014;99(8):738-743. doi: https://doi.org/10.1136/archdischild-2013-304237
13. Maffeis C, Birkebaek NH, Konstantinova M, et al. Prevalence of underweight, overweight, and obesity in children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes: Data from the international SWEET registry. Pediatr Diabetes. 2018;19(7):1211-1220. doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/pedi.12730
14. Belete R, Ataro Z, Abdu A, Sheleme M. Global prevalence of metabolic syndrome among patients with type I diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2021;13(1):25. doi: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13098-021-00641-8
15. Коган-Ясный В.М. Терапевтическое значение инсулина. Программный доклад на IX съезде терапевтов. Л.: Практическая медицина, 1926.
16. Purnell JQ, Braffett BH, Zinman B, et al. Impact of Excessive Weight Gain on Cardiovascular Outcomes in Type 1 Diabetes: Results From the Diabetes Control and Complications Trial/Epidemiology of Diabetes Interventions and Complications (DCCT/EDIC) Study. Diabetes Care. 2017;40(12):1756-1762. doi: https://doi.org/10.2337/dc16-2523
17. Edgerton DS, Lautz M, Scott M, et al. Insulin’s direct effects on the liver dominate the control of hepatic glucose production. J Clin Invest. 2006;116(2):521-7. doi: https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI27073
18. Zaharieva DP, Addala A, Simmons KM, Maahs DM. Weight Management in Youth with Type 1 Diabetes and Obesity: Challenges and Possible Solutions. Curr Obes Rep. 2020;9(4):412-423. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13679-020-00411-z
19. Van der Schueren B, Ellis D, Faradji RN, et al. Obesity in people living with type 1 diabetes. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2021;9(11):776-785. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/S2213-8587(21)00246-1
20. Merger SR, Kerner W, Stadler M, et al. Prevalence and comorbidities of double diabetes. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2016;119:48-56. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diabres.2016.06.003
21. Apperley LJ, Ng SM. Increased insulin requirement may contribute to risk of obesity in children and young people with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus. Diabetes Metab Syndr. 2019;13(1):492-495. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dsx.2018.11.005
22. Климонтов В.В., Юшин А.Ю., Семёнова Ю.Ф., и соавт. Избыточная масса тела и ожирение у больных сахарным диабетом 1 типа: ассоциации с сосудистыми осложнениями и биомаркерами сосудистого ремоделирования // Сахарный диабет. — 2024. — Т. 27. — № 6. — С. 528-535. doi: https://doi.org/10.14341/DM13209
23. Birkebaek NH, Kahlert J, Bjarnason R, et al. Body mass index standard deviation score and obesity in children with type 1 diabetes in the Nordic countries. HbA1c and other predictors of increasing BMISDS. Pediatr Diabetes. 2018;19(7):1198-1205. doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/pedi.12693
24. Fureman AL, Lilja M, Lind T, et al. Comparing continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion and multiple daily injections in children with Type 1 diabetes in Sweden from 2011 to 2016-A longitudinal study from the Swedish National Quality Register (SWEDIABKIDS). Pediatr Diabetes. 2021;22(5):766-775. doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/pedi.13217
25. Tauschmann M, Schwandt A, Prinz N, et al. Three-variate trajectories of metabolic control, body mass index, and insulin dose: Heterogeneous response to initiation of pump therapy in youth with type 1 diabetes. Pediatr Diabetes. 2022;23(3):330-340. doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/pedi.13320
26. El-Jamal S, Elfane H, Chamlal H, et al. Assessment of nutritional status, dietary intake and adherence to dietary recommendations in type 1 diabetic children and adolescents. Rocz Panstw Zakl Hig. 2022;73(3):303-313. doi: https://doi.org/10.32394/rpzh.2022.0222
27. Galli-Tsinopoulou A, Grammatikopoulou MG, Stylianou C, et al. A preliminary case-control study on nutritional status, body composition, and glycemic control of Greek children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes. J Diabetes. 2009;1(1):36-42. doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1753-0407.2008.00002.x
28. Wagner G, Karwautz A. Eating disorders in adolescents with type 1 diabetes mellitus. Curr Opin Psychiatry. 2020;33(6):602-610. doi: https://doi.org/10.1097/YCO.0000000000000650
29. AlOzairi A, Irshad M, AlKandari J, et al. Prevalence and predictors of diabetes distress and depression in people with type 1 diabetes. Front Psychiatry. 2024;15:1367876. doi: https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyt.2024.1367876
30. Kaminsky LA, Dewey D. The association between body mass index and physical activity, and body image, self esteem and social support in adolescents with type 1 diabetes. Can J Diabetes. 2014;38(4):244-9. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcjd.2014.04.005
31. Tran T, Igudesman D, Burger K, et al. Eating behaviors and estimated body fat percentage among adolescents with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2024;207:111070. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diabres.2023.111070
32. Nip ASY, Reboussin BA, Dabelea D, et al. Disordered Eating Behaviors in Youth and Young Adults With Type 1 or Type 2 Diabetes Receiving Insulin Therapy: The SEARCH for Diabetes in Youth Study. Diabetes Care. 2019;42(5):859-866. doi: https://doi.org/10.2337/dc18-2420
33. Elrokhsi SH, Bluez GP, Chin CN, et al. Differences in sleep architecture according to body mass index in children with type 1 diabetes. Pediatr Diabetes. 2020;21(1):98-105. doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/pedi.12918
34. Wilkin TJ. The accelerator hypothesis: weight gain as the missing link between Type I and Type II diabetes. Diabetologia. 2001;44(7):914-22. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s001250100548
35. Nitecki M, Gerstein HC, Balmakov Y, et al. High BMI and the risk for incident type 1 Diabetes Mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis of aggregated cohort studies. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2023;22(1):300. doi: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12933-023-02007-y
36. Li X, Zhu J, Zhao W, et al. The Causal Effect of Obesity on the Risk of 15 Autoimmune Diseases: A Mendelian Randomization Study. Obes Facts. 2023;16(6):598-605. doi: https://doi.org/10.1159/000534468
37. Ciężki S, Kurpiewska E, Bossowski A, Głowińska-Olszewska B. Multi-Faceted Influence of Obesity on Type 1 Diabetes in Children - From Disease Pathogenesis to Complications. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022;13:890833. doi: https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2022.890833
38. Oboza P, Ogarek N, Olszanecka-Glinianowicz M, Kocelak P. Can type 1 diabetes be an unexpected complication of obesity? Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023;14:1121303. doi: https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2023.1121303
39. Ferrara-Cook C, Geyer SM, Evans-Molina C, et al. Excess BMI Accelerates Islet Autoimmunity in Older Children and Adolescents. Diabetes Care. 2020;43(3):580-587. doi: https://doi.org/10.2337/dc19-1167
40. Emet DC, Karavar HN, Gozmen O, et al. Early weight gain after diagnosis may have an impact on remission status in children with new-onset type 1 diabetes mellitus. J Diabetes. 2023;15(12):1011-1019. doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/1753-0407.13455
41. Kurpiewska E, Ciężki S, Jamiołkowska-Sztabkowska M, et al. Excessive BMI is associated with higher C-peptide level at recognition but also with its greater loss in two years clinical observation in children with new onset type 1 diabetes. Front Immunol. 2023;14:1176403. doi: https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2023.1176403
42. Szadkowska A, Pietrzak I, Mianowska B, et al. Insulin sensitivity in Type 1 diabetic children and adolescents. Diabet Med. 2008;25(3):282-8. doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1464-5491.2007.02357.x
43. Cree-Green M, Stuppy JJ, Thurston J, et al. Youth With Type 1 Diabetes Have Adipose, Hepatic, and Peripheral Insulin Resistance. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2018;103(10):3647-3657. doi: https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2018-00433
44. Lu Z, Xiong Y, Feng X, et al. Insulin resistance estimated by estimated glucose disposal rate predicts outcomes in acute ischemic stroke patients. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2023;22(1):225. doi: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12933-023-01925-1
45. Semenova JF, Yushin AY, Korbut AI, Klimontov VV. Glucose Variability in People with Type 1 Diabetes: Associations with Body Weight, Body Composition, and Insulin Sensitivity. Biomedicines. 2024;12(9):2006. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12092006
46. Zeng Q, Chen XJ, He YT, et al. Body composition and metabolic syndrome in patients with type 1 diabetes. World J Diabetes. 2024;15(1):81-91. doi: https://doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v15.i1.81
47. Marques CL, Beretta MV, Prates RE, et al. Body adiposity markers and insulin resistance in patients with type 1 diabetes. Arch Endocrinol Metab. 2023;67(3):401-407. doi: https://doi.org/10.20945/2359-3997000000599
48. DuBose SN, Hermann JM, Tamborlane WV, et al. Obesity in Youth with Type 1 Diabetes in Germany, Austria, and the United States. J Pediatr. 2015;167(3):627-32.e1-4. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpeds.2015.05.046
49. Giandalia A, Russo GT, Ruggeri P, et al. The Burden of Obesity in Type 1 Diabetic Subjects: A Sex-specific Analysis From the AMD Annals Initiative. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2023;108(11):e1224-e1235. doi: https://doi.org/10.1210/clinem/dgad302
50. Özkaya V, Özkaya ŞÖ, Adal SE. Relationship between visceral adiposity index and glycemic and metabolic control in children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes mellitus. Ir J Med Sci. 2024;193(1):181-189. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11845-023-03375-w
51. Genua I, Franch-Nadal J, Navas E, et al. Obesity and related comorbidities in a large population-based cohort of subjects with type 1 diabetes in Catalonia. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022;13:1015614. doi: https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2022.1015614
52. Clinck I, Mertens J, Wouters K, et al. Insulin resistance and CGM-derived parameters in people with type 1 diabetes: are they associated? J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2024; in press. dgae015. doi: https://doi.org/10.1210/clinem/dgae015
53. Lalanne-Mistrih ML, Bonhoure A, Messier V, et al. Overweight and Obesity in People Living With Type 1 Diabetes: A Cross-Sectional Analysis of the BETTER Registry. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2024;40(6):e3837. doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/dmrr.3837
54. Petty LD, Soto-Pedre E, McCrimmon RJ, Pearson ER. Body Mass Index’s influence on arterial hypertension in Type 1 diabetes - A brief report from IMI-SOPHIA study. J Diabetes Complications. 2024;38(6):108747. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jdiacomp.2024.108747
55. Moosaie F, Ghaemi F, Mechanick JI, et al. Obesity and Diabetic Complications: A Study from the Nationwide Diabetes Report of the National Program for Prevention and Control of Diabetes (NPPCD-2021) Implications for Action on Multiple Scales. Prim Care Diabetes. 2022;16(3):422-429. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pcd.2022.03.009
56. Parente EB, Harjutsalo V, Forsblom C, Groop PH; FinnDiane Study Group. The impact of central obesity on the risk of hospitalization or death due to heart failure in type 1 diabetes: a 16-year cohort study. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2021;20(1):153. doi: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12933-021-01340-4
57. Chillarón JJ, Goday A, Flores-Le-Roux JA, et al. Estimated glucose disposal rate in assessment of the metabolic syndrome and microvascular complications in patients with type 1 diabetes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2009;94(9):3530-4. doi: https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2009-0960
58. Garofolo M, Gualdani E, Scarale MG, et al. Insulin Resistance and Risk of Major Vascular Events and All-Cause Mortality in Type 1 Diabetes: A 10-Year Follow-up Study. Diabetes Care. 2020;43(10):e139-e141. doi: https://doi.org/10.2337/dc20-0433
59. Sun R, Wang J, Li M, et al. Association of Insulin Resistance With Cardiovascular Disease and All-Cause Mortality in Type 1 Diabetes: Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Diabetes Care 2024:dc240475. doi: https://doi.org/10.2337/dc24-0475
60. Grzelka-Woźniak A, Uruska A, Szymańska-Garbacz E, et al. Indirect insulin resistance markers are associated with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in type 1 diabetes. Pol Arch Intern Med. 2023;133(5):16404. doi: https://doi.org/10.20452/pamw.16404
61. Mantovani A, Morieri ML, Aldigeri R, et al. MASLD, hepatic steatosis and fibrosis are associated with the prevalence of chronic kidney disease and retinopathy in adults with type 1 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Metab. 2024;50(1):101497. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diabet.2023.101497
62. Lee AS, Twigg SM, Flack JR. Metabolic syndrome in type 1 diabetes and its association with diabetes complications. Diabet Med. 2021;38(2):e14376. doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/dme.14376
63. Igudesman D, Crandell J, Corbin KD, et al. Weight management in young adults with type 1 diabetes: The advancing care for type 1 diabetes and obesity network sequential multiple assignment randomized trial pilot results. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2023;25(3):688-699. doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/dom.14911
64. Güneş Kaya D, Arslan N, Ayyıldız F, et al. The potential of the Mediterranean diet to improve metabolic control and body composition in youths with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus. BMC Endocr Disord. 2024;24(1):63. doi: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12902-024-01593-6
65. Huerta-Uribe N, Hormazábal-Aguayo IA, Izquierdo M, García-Hermoso A. Youth with type 1 diabetes mellitus are more inactive and sedentary than apparently healthy peers: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2023;200:110697. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diabres.2023.110697
66. Muntis FR, Igudesman D, Sarteau AC, et al. Relationship Between Moderate-to-Vigorous Physical Activity and Glycemia Among Young Adults with Type 1 Diabetes and Overweight or Obesity: Results from the Advancing Care for Type 1 Diabetes and Obesity Network (ACT1ON) Study. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2022;24(12):881-891. doi: https://doi.org/10.1089/dia.2022.0253
67. Freeby M, Lane K. Treating obesity in type 1 diabetes mellitus - review of efficacy and safety. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes. 2024;31(1):1-7. doi: https://doi.org/10.1097/MED.0000000000000841
68. Liu YS, Chen CN, Chen ZG, et al. Vascular and metabolic effects of metformin added to insulin therapy in patients with type 1 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2020;36(6):e3334. doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/dmrr.3334
69. Tandon S, Ayis S, Hopkins D, et al. The impact of pharmacological and lifestyle interventions on body weight in people with type 1 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2021;23(2):350-362. doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/dom.14221
70. Danne T, Garg S, Peters AL, et al. International Consensus on Risk Management of Diabetic Ketoacidosis in Patients With Type 1 Diabetes Treated With Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter (SGLT) Inhibitors. Diabetes Care. 2019;42(6):1147-1154. doi: https://doi.org/10.2337/dc18-2316
71. Dejgaard TF, Schmidt S, Frandsen CS, et al. Liraglutide reduces hyperglycaemia and body weight in overweight, dysregulated insulin-pump-treated patients with type 1 diabetes: The Lira Pump trial-a randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled trial. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2020;22(4):492-500. doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/dom.13911
72. Garg SK, Akturk HK, Kaur G, et al. Efficacy and Safety of Tirzepatide in Overweight and Obese Adult Patients with Type 1 Diabetes. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2024;26(6):367-374. doi: https://doi.org/10.1089/dia.2024.0050
73. Edwards K, Li X, Lingvay I. Clinical and Safety Outcomes With GLP-1 Receptor Agonists and SGLT2 Inhibitors in Type 1 Diabetes: A Real-World Study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2023;108(4):920-930. doi: https://doi.org/10.1210/clinem/dgac618
74. Kermansaravi M, Valizadeh R, Jazi AD, et al. Current Status of Metabolic/Bariatric Surgery in Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus: an Updated Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Obes Surg. 2022;32(5):1726-1733. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11695-022-05980-7
75. Abi Mosleh K, Salameh Y, Ghusn W, et al. Impact of metabolic and bariatric surgery on weight loss and insulin requirements in type 1 and insulin-treated type 2 diabetes. Clin Obes. 2024:e12689; in press. doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/cob.1268
76. Korakas E, Kountouri A, Raptis A, et al. Bariatric Surgery and Type 1 Diabetes: Unanswered Questions. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2020;11:525909. doi: https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2020.525909
Об авторах
В. В. КлимонтовРоссия
Климонтов Вадим Валерьевич - д.м.н., профессор; eLibrary SPIN: 1734-4030; WoS Researcher ID: R-7689-2017; Scopus Author ID: 8295977000.
630060, Новосибирск, ул. Тимакова, д. 2
Конфликт интересов:
Авторы декларируют отсутствие явных и потенциальных конфликтов интересов, связанных с публикацией настоящей статьи
А. Ю. Юшин
Россия
Юшин Антон Юрьевич - м.н.с.
Новосибирск
Конфликт интересов:
Авторы декларируют отсутствие явных и потенциальных конфликтов интересов, связанных с публикацией настоящей статьи
Дополнительные файлы
|
|
1. Рисунок 1. Ожирение как фактор риска осложнений и неблагоприятных исходов при сахарном диабете 1 типа. | |
| Тема | ||
| Тип | Исследовательские инструменты | |
Посмотреть
(234KB)
|
Метаданные ▾ | |
Рецензия
Для цитирования:
Климонтов В.В., Юшин А.Ю. Ожирение у больных сахарным диабетом 1 типа: причины и следствия. Сахарный диабет. 2025;28(4):394-403. https://doi.org/10.14341/DM13237
For citation:
Klimontov V.V., Yushin A.Yu. Obesity in Patients with Type 1 Diabetes: Causes and Consequences. Diabetes mellitus. 2025;28(4):394-403. (In Russ.) https://doi.org/10.14341/DM13237

Контент доступен под лицензией Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0).















































